/ Was ist eine Cloud Native App Protection Platform (CNAPP)?
Was ist eine Cloud Native App Protection Platform (CNAPP)?
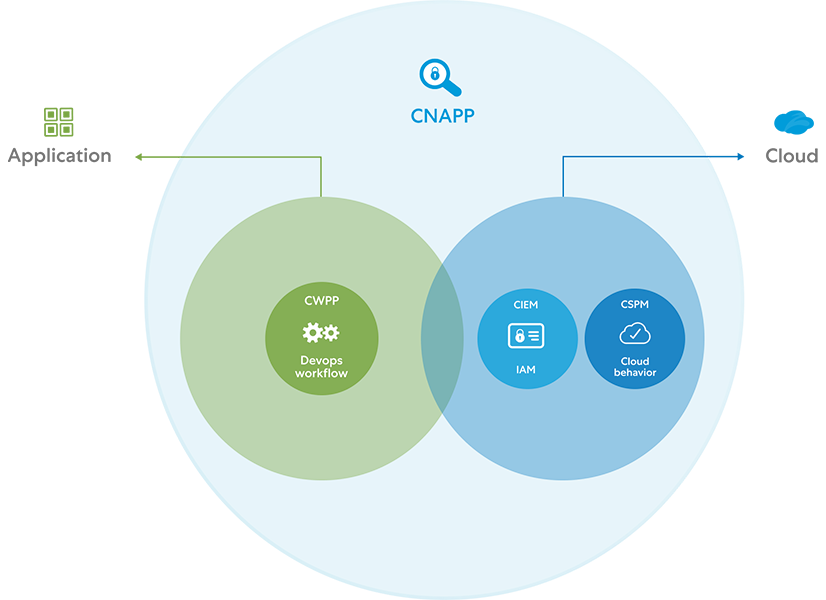
Eine Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) ist eine Sicherheits- und Compliance-Lösung, die die Erstellung, Bereitstellung und Ausführung sicherer Cloud-nativer Anwendungen in den heute gängigen hochgradig automatisierten und dynamischen öffentlichen Cloud-Umgebungen ermöglicht. CNAPPs unterstützen Sicherheitsteams außerdem bei der effektiveren Zusammenarbeit mit Entwicklern und DevOps-Partnern. Mit CNAPPs steht Unternehmen eine neue Kategorie von Cloud-Sicherheitsplattform zur Verfügung, die CSPM, CIEM, IAM, CWPP sowie Data Protection und andere Funktionen kombiniert.
Warum sind CNAPPs ein wichtiges Thema?
Herkömmliche Sicherheitskonzepte und -tools wurden für On-Premise-Rechenzentren und lokal installierte Endgeräte entwickelt. Sie bieten keinen zuverlässigen Schutz für Cloud-native Anwendungen und Services. Die Umstellung auf Cloud-native Technologien, dynamische, kurzlebige und stark automatisierte Umgebungen, kürzere Release-Zyklen und moderne Entwicklungsansätze (Infrastructure as Code [IaC], CI/CD-Pipelines, Container, serverlose Funktionen, Kubernetes usw.) macht eine entsprechende Transformation der IT-Sicherheit erforderlich.
Die öffentliche Cloud verändert sich ständig. Sicherheitsteams stehen vor der Herausforderung, unter diesen Voraussetzungen Sicherheit und Compliance zu gewährleisten, idealerweise ohne organisationsinterne Abläufe zu verlangsamen. Um dies zu erreichen, müssen sie Sicherheitsprobleme und ‑risiken frühzeitig in der Entwicklung erkennen, diese schnellstmöglich beheben und für kontinuierliche, konsistente Absicherung sorgen. Aufgrund der komplexen Abhängigkeiten moderner Umgebungen ist es mit herkömmlichen Ansätzen jedoch nur schwer möglich, ein solches Vorhaben umzusetzen.
Durch Optimierung der Sicherheit und Compliance für Cloud-Umgebungen können Sicherheitsexperten das DevOps-Team unterstützen und eine möglichst reibungslose Zusammenarbeit fördern. Dies erfordert jedoch eine Abkehr von der bisherigen Fokussierung auf den Schutz von Infrastrukturen – und einen Mentalitätswandel hin zum neuen Konzept des Schutzes von Anwendungen, die auf Workloads laufen. Die Absicherung der Cloud-Service-Konfigurationen und Produktivumgebung ist die Mindestvoraussetzung. Als zusätzliche Sicherheitsschicht empfiehlt sich auch ein Laufzeitschutz.
Hauptbestandteile einer CNAPP
Eine effektive CNAPP unterstützt Sicherheitsteams dabei, Informationen aus einer Vielzahl von Signalen in einer einzigen Ansicht zu korrelieren, um die schwerwiegendsten Risiken für die Organisation zu erkennen und entsprechend zu priorisieren. CNAPPs kombinieren eine Reihe von Funktionen:
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) zur Überwachung, Erkennung und Behebung von Compliance-Risiken und Fehlkonfigurationen in Cloud-Umgebungen sowie Ausgabe rechtzeitiger Warnmeldungen
- Sicherheit für Infrastructure-as-Code zur frühzeitigen Erkennung von Fehlkonfigurationen im Software-Entwicklungszyklus und Verhinderung von Sicherheitsrisiken bei der Ausführung
- Compliance und Governance zur Verwaltung des Compliance-Status sowie zur Behebung von Konfigurationsabweichungen und Richtlinienverstößen in Multicloud-Umgebungen
- Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) zur Minderung des Risikos von Datenpannen in öffentlichen Clouds durch kontinuierliche Überwachung sämtlicher Berechtigungen und Aktivitäten
- Data Protection-Funktionen zur Überwachung, Klassifizierung und Überprüfung von Daten und zur Verhinderung der Exfiltration kritischer Daten infolge von Phishing, Insider-Bedrohungen und anderen Cyberangriffen
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) zur Kontrolle des Zugriffs auf interne Ressourcen, um sicherzustellen, dass User-Berechtigungen einen angemessenen Zugriff auf Systeme und Daten ermöglichen
- Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP) zur Gewährleistung von Transparenz und Kontrolle über physische Computer, VMs, Container und serverlose Workloads in hybriden, Multicloud- und Rechenzentrumsumgebungen
Probleme von Legacy-Ansätzen
Das Unternehmenswachstum führt häufig zu einem Flickenteppich aus Einzellösungen und disparaten Sicherheitskontrollen in mehreren Cloud-Umgebungen. Sicherheitsteams setzen ein ganzes Arsenal verschiedener Tools bestehend aus CSPM, CIEM, CWPP usw. zum Schutz von Cloud-Infrastrukturen und Produktivumgebungen ein. Im Ergebnis erschwert dies die effektive Erkennung, Priorisierung und Behebung von Risiken. Verantwortlich dafür sind verschiedene Risikofaktoren:
- Transparenzlücken und tote Winkel
- Bezug von Daten aus unterschiedlichen Quellen anstelle eines allgemeingültigen Datenbestands („Single Source of Truth“)
- Informationsüberflutung und hoher Zeitaufwand für die Datenkorrelation
- Alarmmüdigkeit ohne zuverlässige Methode zur Priorisierung dringender Probleme
- Mangel an Ressourcen, technischem Fachwissen und Schulungen für die einzelnen Tools
- betriebliche Komplexität und hohe Kosten durch separate Verwaltung unterschiedlicher Einzelprodukte
Der Versuch, zuverlässige Kontrollmaßnahmen mit einer ganzen Palette unterschiedlicher Tools in komplexen Umgebungen umzusetzen, ist mit einem hohen Zeit-, Ressourcen- und Arbeitsaufwand verbunden – und häufig zum Scheitern verurteilt.
Vorteile von CNAPPs
Als ganzheitliche Sicherheitslösung stellt eine CNAPP lückenlosen Schutz bereit. Auch kurzlebige, serverlose und Container-Umgebungen werden zuverlässig abgesichert. So profitieren Sie gleich von mehreren Vorteilen:
- Zentrale Management-Konsole: Dient zur Optimierung der teamübergreifenden Zusammenarbeit und Effizienz, indem Zusammenhänge zwischen kleineren Problemen, isolierten Sicherheitsvorfällen und schwer erkennbaren Angriffsvektoren in intuitiven Diagrammen dargestellt und mit Warnmeldungen, Empfehlungen sowie Anleitungen zur Behebung aufbereitet werden, um fundierte Entscheidungsprozesse zu unterstützen.
- Reduzierte Komplexität und Betriebskosten: Statt unterschiedliche Einzelprodukte zu verwalten, erhalten Sie einen ganzheitlichen Überblick über das Risikoprofil mit lückenloser Transparenz über alle Konfigurationen, Assets, Berechtigungen, Codes und Workloads hinweg. Eine CNAPP analysiert Millionen von Attributen, um die schwerwiegendsten Risiken zu priorisieren.
- Umfassender Schutz für alle Cloud-Umgebungen und Services: Durch transparenten Einblick in die gesamte Multicloud-Infrastruktur – inklusive IaaS und PaaS – mit allen VMs, Containern, serverlosen Workloads und Entwicklungsumgebungen können Sie Sicherheitsrisiken frühzeitig erkennen und beheben.
- Zuverlässige Sicherheit in DevOps-Geschwindigkeit: Mittels Integration mit IDE-Plattformen werden Fehlkonfigurationen und Compliance-Probleme bereits in der Entwicklungsphase bzw. im Rahmen von CI/CD-Workflows erkannt. Integrationen mit SecOps-Ökosystemen unterstützen zusätzlich die Auslösung von Warnmeldungen, Tickets und Workflows zur umgehenden Behebung von Verstößen.
- Guardrails zur Gewährleistung geteilter Sicherheitsverantwortung: Durch native Integrationen mit vorhandenen Entwicklungs- und DevOps-Tools werden Sicherheitskontrollen in sämtlichen Ebenen des DevOps-Zyklus eingefügt. Die Implementierung von Guardrails ermöglicht Entwicklern, mehr Verantwortung für die sicherheitsrelevanten Aspekte ihrer Arbeit zu übernehmen. Dadurch werden Spannungen zwischen Sicherheits- und DevOps-Teams abgebaut und effiziente DevSecOps-Workflows unterstützt.
Wie funktioniert eine CNAPP?
CNAPPs reduzieren Komplexität und Betriebskosten, da sie mehrere Sicherheitstools und Sicherheitsfunktionen in einer Plattform vereinen. Im Einzelnen werden folgende Leistungen bereitgestellt:
- kombinierter Funktionsumfang von CSPM-, CIEM- und CWPP-Tools
- Korrelation von Schwachstellen, Kontext und Beziehungen im gesamten Entwicklungszyklus
- Erkennung von Risiken hoher Priorität und Lieferung von umfangreichem Kontext
- Schritt-für-Schritt-Anweisungen und automatische Maßnahmen zur Behebung von Schwachstellen und Fehlkonfigurationen
- Guardrails zur Verhinderung nicht genehmigter Änderungen an der Architektur
- einfache Integration mit SecOps-Ökosystemen zum Senden von Warnungen nahezu in Echtzeit
Funktionsumfang einer CNAPP (Bild übernommen aus: „How to Protect Your Clouds with CSPM, CWPP, CNAPP, and CASB“, Gartner, 6. Mai 2021)
Kernfunktionen einer CNAPP
CNAPPs vereinen die Funktionen zahlreicher Sicherheits- und Compliance-Tools. Entsprechend profitieren Unternehmen, die auf diese Technologie umsteigen, von einem umfassenden Leistungsspektrum.
Absicherung der Multicloud-Infrastruktur
Eine CNAPP gewährleistet komplette Transparenz über alle Anwendungen, APIs, Cloud-Ressourcen, Identitäten und sensiblen Daten in der Infrastruktur. Sie liefert Auskunft darüber, ob Ressourcen in AWS, Azure und Google Cloud datenschutzkonform sind, und unterstützt die Priorisierung von Fehlerbehebungsmaßnahmen auf der Basis zuverlässiger Risikobewertung.
Absicherung der Produktivumgebung
Mit einer CNAPP können Sicherheitslösungen bereits in den Anfangsphasen des Entwicklungszyklus eingesetzt („nach links verlagert“) werden. DevOps-Experten werden stärkere Tools zur frühzeitigen Erkennung und schnellen Behebung von Bedrohungen und Sicherheitsrisiken an die Hand gegeben. So lässt sich gewährleisten, dass Anwendungen und Verfahren zur Datenverarbeitung alle geltenden Vorschriften erfüllen.
Absicherung von Workloads
Sicherheitsrisiken und Fehlkonfigurationen lassen sich einfacher erkennen und beheben. Außerdem stellt die Plattform Funktionen zur netzwerkbasierten Verhaltensanalyse, Richtlinien-Durchsetzung und identitätsbasierten Segmentierung von Cloud-Workloads bereit.
Kontinuierliche Governance und Compliance
Automatische Sicherheitskontrollen überwachen die kontinuierliche Compliance und Governance von Daten, Konfigurationen und Berechtigungen.
Verbesserte teamübergreifende Zusammenarbeit
Durch Integration von gängigen Workflows, Datenkorrelation, aussagekräftigen Analyseergebnissen und Maßnahmen zur Fehlerbehebung wird eine reibungslose Zusammenarbeit zwischen den für DevSecOps, DevOps und Cloud-Sicherheit zuständigen Teams gefördert.
Empfehlungen von Gartner zu CNAPP
Der Gartner-Report „Innovation Insight for Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms“ enthält folgende Empfehlung: „Anstatt Entwicklungs- und Laufzeitumgebungen als separate Problembereiche zu betrachten, die jeweils mit einer Kombination unterschiedlicher Tools abgesichert und gescannt werden, sollten Sicherheit und Compliance als ein Kontinuum begriffen werden, das den gesamten Lebenszyklus umfasst. Entsprechend ist eine möglichst umfassende Konsolidierung anzustreben.“
Daraus ergeben sich mehrere konkrete Handlungsempfehlungen:
- Implementieren eines integrierten Sicherheitskonzepts für den gesamten Lebenszyklus Cloud-nativer Anwendungen von der Entwicklung bis zum Einsatz in Produktivumgebungen
- Priorisieren der Risikobehebung durch umfassendes Scannen aller Entwicklungsartefakte und Cloud-Konfigurationen sowie lückenlose Überwachung der Laufzeitumgebung und Konfigurationen
- Bewertung neuer CNAPP-Angebote als Alternative zu CSPM und CWPP; das Ablaufen einschlägiger Verträge sollte als Chance zur Reduzierung der Komplexität durch Konsolidierung der Anbieter genutzt werden
CNAPP von Zscaler
Posture Control™ von Zscaler ist eine leistungsstarke CNAPP, die einen radikal neuen Ansatz zum Schutz Cloud-nativer Anwendungen darstellt. Die komplett agentenlose Lösung korreliert Informationen aus mehreren Sicherheitsengines zur Priorisierung verborgener Risiken aufgrund von Fehlkonfigurationen, Bedrohungen und Sicherheitslücken im gesamten Cloud-Stack. Dadurch werden Kosten und Komplexität reduziert sowie Reibungspunkte zwischen einzelnen Abteilungen abgebaut.
Unsere ganzheitliche Plattform wurde von Grund auf für die Priorisierung von Sicherheitsrisiken in distribuierten Clouds sowie den Schutz von Infrastrukturen und Anwendungen in allen Phasen des Entwicklungs- und DevOps-Zyklus konzipiert und entwickelt. Sie kombiniert Funktionen zur Gewährleistung eines unübertroffenen Schutzniveaus für alle wichtigen Anwendungsszenarien:
- Schutz für Konfigurationen: Die Lösung unterstützt die Einrichtung und Verwaltung umfassender CSPM-Kontrollen für sämtliche Cloud-Infrastrukturen, Ressourcen, Daten und Identitäten. Mehr erfahren
- Schutz für Berechtigungen:Identitäten der User und Computer werden unter Durchsetzung minimaler Rechtevergabe geschützt. Weitere Informationen
- Schutz für Infrastructure-as-Code: Schwachstellen und Compliance-Probleme lassen sich im Rahmen einer „Linksverlagerung“ der Sicherheitsfunktionen bereits im Entwicklungs- bzw. DevOps-Zyklus beheben. Weitere Informationen
- Schutz für Daten: Vertrauliche Daten werden in allen Cloud-Repositorys zuverlässig unter Gewährleistung von Transparenz, Kontrolle und Compliance geschützt. Mehr erfahren
- Schutz für Workloads und Anwendungen: Hosts, Container (z. B. Kubernetes) und serverlose Funktionen werden mit Zero-Trust-Schutz in allen Phasen des Anwendungszyklus ohne Agent-Installation abgesichert. Mehr erfahren



