Key Takeaways: An in-depth analysis of Midas and trends across other Thanos ransomware variants reveals how ransomware groups shifted tactics in 2021 to:
- lower sunk costs by using RaaS builders to reduce development time
- increase payouts with double extortion tactics by using their own data leak sites
- extend the length and effectiveness of campaigns to get the highest investment returns by updating payloads and/or rebranding their own ransomware group
Advertised on the darkweb for Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS), Thanos ransomware was first identified in February 2020. Written in C# language running on the .net framework, this serious offender reboots systems in safeboot mode to bypass antivirus detection and includes a builder that enables threat actors to create new variants by customizing samples. Source code of Thanos builder also leaked and there are lots of different variants that have been seen based on that. Here we discuss the four 2021 variants shown in Figure 1 below that used double extortion tactics.
Figure 1:Timeline of Thanos derived ransomware variations
Beginning in February 2021, the Prometheus ransomware variant emerged as one of the new Thanos built variants of the year. It encrypts files and appends “.[{ID}],.PROM[prometheushelp@mail{.}ch] , {ID}[prometheusdec@yahoo{.}com] “ extension and drop “RESTORE_FILES_INFO.txt, RESTORE_FILES_INFO.hta” ransom note. The Prometheus group which operates the variant has claimed to be part of the notorious REvil ransomware group responsible for the Kaseya supply chain attack, however experts doubt the claim as a solid connection between the two has never been established. This variant is known for using double extortion techniques to make organizations pay that include threatening to leak valuable data on their leak site. A quick check reveals that the leak site is currently down, but the threat still holds potential weight
In July 2021, another Thanos derived ransomware called Haron was discovered. It encrypts files and appends “.{Targeted Company name}” extension and drops “RESTORE_FILES_INFO.hta,RESTORE_FILES_INFO.txt” ransom note. Haron ransomware group also have their own data leak site used for double extortion. This variant has striking similarities with Avaddon ransomware based on examination of the ransom note and data leak site information.
September 2021, the Thanos builder was used again to develop the Spook ransomware variant. It encrypts files and appends “.{ID}” extension and drops “RESTORE_FILES_INFO.hta,RESTORE_FILES_INFO.txt” ransom note. Similar to the other variants, Spook ransomware also uses double extortion techniques with their own data leak site as shown in the screenshot below.
Rounding out the year in October 2021, another Thanos ransomware family emerged with the Midas variant that appends “.{Targeted Company name}” extension and drops “RESTORE_FILES_INFO.hta and RESTORE_FILES_INFO.txt” ransom note. In January 2022, ThreatLabz investigated a report of Midas ransomware being slowly deployed over a 2-month period and the attacker was observed using different powershell scripts, remote access tools and an open source windows utility.
Like the others, Midas features its own data leak site for double extortion. Interestingly, the site contains leaked victim data from a Haron ransomware attack, suggesting to researchers that Midas is potentially linked to the Haron ransomware operators.
Figure 2: Count of companies with leaked data by 2021 Thanos ransomware variants.
Identifying Thanos as the Source for the Prometheus, Haron, Spook, and Midas ransomware variants
Tracing the evolution of Thanos based ransomware variants back to the source provides threat researchers with an inside look at how ransomware gangs operate and evolve over time. To establish a connection between each variant, the ThreatLabz team looked for the use of common signatures and indicators that would point back to the Thanos ransomware builder. After determining that each variant was derived using the builder, the team set about analyzing the similarities and differences in the shifting techniques adversaries employ to make new variants of a common origin ransomware more effective. These observations help us to gain insights into the cooperation happening between adversary groups and better understand the development lifecycle and alternating impacts of ransomware through its variants.
The analysis that follows walks you through identifying Thanos variants through an examination of common signatures found in the ransom note key identifiers and the consistent use of a common file marker “GotAllDone”. Followed by an in-depth analysis of the latest Midas variant.
Identifying Thanos Variants
All four of the 2021 Thanos based ransomware variants contain a key identifier with common signatures for the Thanos builder found in the ransom notes as shown in Figure 3 below.
|
|
|
|
Figure 3: Screenshots of ransom notes showing the common signature ‘Key Identifier’ for 2021 Thanos ransomware variants: Prometheus, Haron, Spook and Midas.
Another similarity is that after encryption they append base 64 encoded key after encrypting data of every file. Prometheus, Haron, Spook, and Midasall contain the same FileMarker that is “GotAllDone” appended at the end of each encrypted file. Below screenshot displays the FileMarker info and Base64 encoded key appended after the data encrypted by Midas ransomware.
Figure 4: Screenshots of FileMarker and Base64 encoded key appended
Midas Ransomware
The Midas data leak site currently displays data from 29 victim companies including data from several victims previously seen on the Haron data leak site which is now inactive.
Figure 5: Screenshot of the Midas ransomware data leak site index page.
Figure 6: Screenshot of victim companies listed on Midas ransomware data leak site.
Technical analysis
Midas ransomware is written in C# and obfuscated using smartassembly. Once executed this variant starts terminating processes using taskkill.exe. It terminates processes that inhibit encryption processes and processes related to security software, database related programs so it can encrypt more files. Below is a list of the common processes typically terminated by Thanos based ransomware.
Most commonly terminated processes:
|
RaccineSettings.exe mspub.exe CNTAoSMgr.exe xfssvccon.exe mydesktopqos.exe sqlbrowser.exe sqlwriter.exe tbirdconfig.exe visio.exe sqlservr.exe sqbcoreservice.exe thebat64.exe mysqld.exe dbeng50.exe Ntrtscan.exe |
isqlplussvc.exe synctime.exe firefoxconfig.exe winword.exe ocomm.exe agntsvc.exe infopath.exe ocautoupds.exe mysqld-opt.exe sqlagent.exe powerpnt.exe steam.exe zoolz.exe encsvc.exe thebat.exe |
tmlisten.exe mbamtray.exe PccNTMon.exe mydesktopservice.exe excel.exe onenote.exe msftesql.exe wordpad.exe ocssd.exe mysqld-nt.exe oracle.exe dbsnmp.exe outlook.exe msaccess.exe |
It also deletes the process, schedule task and registry related to the Raccine tool. It is a ransomware prevention tool that protects the system from ransomware processes to delete shadow copy.
Prometheus, Haron, Spook and Midas have been seen terminating Raccine related artifacts.
Figure 7: Command used to terminate Vaccine process and other artifacts.
The Midas variant is designed to stop service related to security products, database software, backups and email exchanges.
List of most commonly disrupted services:
| start Dnscache /y | stop msexchangeimap4 /y |
stop MSSQLServerADHelper /y |
| start FDResPub /y | stop ARSM /y |
stop McAfeeEngineService /y |
| start SSDPSRV /y | stop MSSQL$BKUPEXEC /y |
stop VeeamHvIntegrationSvc /y |
| start upnphost /y | stop unistoresvc_1af40a /y |
stop MSSQLServerADHelper100 /y |
| stop avpsus /y | stop BackupExecAgentAccelerator /y |
stop McAfeeFramework /y |
| stop McAfeeDLPAgentService /y | stop MSSQL$ECWDB2 /y |
stop VeeamMountSvc /y |
| stop mfewc /y | stop audioendpointbuilder /y |
stop MSSQLServerOLAPService /y |
| stop BMR Boot Service /y | stop BackupExecAgentBrowser /y |
stop McAfeeFrameworkMcAfeeFramework /y |
| stop NetBackup BMR MTFTP Service /y | stop MSSQL$PRACTICEMGT /y | stop VeeamNFSSvc /y |
| stop DefWatch /y | stop BackupExecDeviceMediaService /y | stop MySQL57 /y |
| stop ccEvtMgr /y | stop MSSQL$PRACTTICEBGC /y | stop McShield /y |
| stop ccSetMgr /y | stop BackupExecJobEngine /y |
stop VeeamRESTSvc /y |
| stop SavRoam /y | stop MSSQL$PROD /y | stop MySQL80 /y |
| stop RTVscan /y | stop AcronisAgent /y |
stop McTaskManager /y |
| stop QBFCService /y | stop BackupExecManagementService /y |
stop VeeamTransportSvc /y |
| stop QBIDPService /y | stop MSSQL$PROFXENGAGEMENT /y |
stop OracleClientCache80 /y |
| stop Intuit.QuickBooks.FCS /y | stop Antivirus /y | stop mfefire /y |
| stop QBCFMonitorService /y | stop BackupExecRPCService /y | stop wbengine /y |
| stop YooBackup /y | stop MSSQL$SBSMONITORING / |
stop ReportServer$SQL_2008 /y |
| stop YooIT /y | stop MSSQL$SBSMONITORING /y | stop mfemms /y |
| stop zhudongfangyu /y | stop AVP /y | stop wbengine /y |
| stop stc_raw_agent /y | stop BackupExecVSSProvider /y | stop RESvc /y |
| stop VSNAPVSS /y | stop MSSQL$SHAREPOINT /y | stop mfevtp /y |
| stop VeeamTransportSvc /y | stop DCAgent /y |
stop sms_site_sql_backup /y |
| stop VeeamDeploymentService /y | stop bedbg /y |
stop SQLAgent$BKUPEXEC /y |
| stop VeeamNFSSvc /y | stop MSSQL$SQL_2008 /y |
stop MSSQL$SOPHOS /y |
| stop veeam /y | stop EhttpSrv /y |
stop SQLAgent$CITRIX_METAFRAME /y |
| stop PDVFSService /y | stop MMS /y | stop sacsvr /y |
| stop BackupExecVSSProvider /y | stop MSSQL$SQLEXPRESS /y |
stop SQLAgent$CXDB /y |
| stop BackupExecAgentAccelerator /y | stop ekrn /y |
stop SAVAdminService /y |
| stop BackupExecAgentBrowser /y | stop mozyprobackup /y |
stop SQLAgent$ECWDB2 /y |
| stop BackupExecDiveciMediaService /y | stop MSSQL$SYSTEM_BGC /y | stop SAVService /y |
| stop BackupExecJobEngine /y | stop EPSecurityService /y |
stop SQLAgent$PRACTTICEBGC /y |
| stop BackupExecManagementService /y | stop MSSQL$VEEAMSQL2008R2 /y |
stop SepMasterService /y |
| stop BackupExecRPCService /y | stop MSSQL$TPS /y |
stop SQLAgent$PRACTTICEMGT /y |
| stop AcrSch2Svc /y | stop EPUpdateService /y | stop ShMonitor /y |
| stop AcronisAgent /y | stop ntrtscan /y |
stop SQLAgent$PROD /y |
| stop CASAD2DWebSvc /y | stop MSSQL$TPSAMA /y | stop Smcinst /y |
| stop CAARCUpdateSvc /y | stop EsgShKernel /y |
stop SQLAgent$PROFXENGAGEMENT /y |
| stop sophos /y | stop PDVFSService /y | stop SmcService /y |
| stop MsDtsServer /y | stop MSSQL$VEEAMSQL2008R2 /y |
stop SQLAgent$SBSMONITORING /y |
| stop IISAdmin /y | stop ESHASRV /y | stop SntpService /y |
| stop MSExchangeES /y | stop SDRSVC /y |
stop SQLAgent$SHAREPOINT /y |
| stop EraserSvc11710 /y | stop MSSQL$VEEAMSQL2012 /y | stop sophossps /y |
| stop MsDtsServer100 /y | stop FA_Scheduler /y |
stop SQLAgent$SQL_2008 /y |
| stop NetMsmqActivator /y | stop SQLAgent$VEEAMSQL2008R2 /y |
stop SQLAgent$SOPHOS /y |
| stop MSExchangeIS /y | stop MSSQLFDLauncher$PROFXENGAGEMENT /y |
stop SQLAgent$SQLEXPRESS /y |
| stop SamSs /y | stop KAVFS /y | stop svcGenericHost /y |
| stop ReportServer /y | stop SQLWriter /y |
stop SQLAgent$SYSTEM_BGC /y |
| stop MsDtsServer110 /y | stop MSSQLFDLauncher$SBSMONITORING /y | stop swi_filter /y |
| stop POP3Svc /y | stop KAVFSGT /y | stop SQLAgent$TPS /y |
| stop MSExchangeMGMT /y | stop VeeamBackupSvc /y | stop swi_service /y |
| stop SMTPSvc /y | stop MSSQLFDLauncher$SHAREPOINT /y |
stop SQLAgent$TPSAMA /y |
| stop ReportServer$SQL_2008 /y | stop kavfsslp /y | stop swi_update /y |
| stop msftesql$PROD /y | stop VeeamBrokerSvc /y |
stop SQLAgent$VEEAMSQL2008R2 /y |
| stop SstpSvc /y | stop MSSQLFDLauncher$SQL_2008 /y | stop swi_update_64 /y |
| stop MSExchangeMTA /y | stop klnagent /y |
stop SQLAgent$VEEAMSQL2012 /y |
| stop ReportServer$SYSTEM_BGC /y | stop VeeamCatalogSvc /y | stop TmCCSF /y |
| stop MSOLAP$SQL_2008 /y | stop MSSQLFDLauncher$SYSTEM_BGC /y | stop SQLBrowser /y |
| stop UI0Detect /y | stop macmnsvc /y | stop tmlisten /y |
| stop MSExchangeSA /y | stop VeeamCloudSvc /y |
stop SQLSafeOLRService /y |
| stop ReportServer$TPS /y | stop MSSQLFDLauncher$TPS /y | stop TrueKey /y |
| stop MSOLAP$SYSTEM_BGC /y | stop masvc /y |
stop SQLSERVERAGENT /y |
| stop W3Svc /y | stop VeeamDeploymentService /y |
stop TrueKeyScheduler /y |
| stop MSExchangeSRS /y | stop MSSQLFDLauncher$TPSAMA /y |
stop SQLTELEMETRY /y |
| stop ReportServer$TPSAMA /y | stop MBAMService /y |
stop TrueKeyServiceHelper /y |
| stop MSOLAP$TPS /y | stop VeeamDeploySvc /y |
stop SQLTELEMETRY$ECWDB2 /y |
| stop msexchangeadtopology /y | stop MSSQLSERVER /y | stop WRSVC /y |
| stop AcrSch2Svc /y | stop MBEndpointAgent /y |
stop mssql$vim_sqlexp /y |
| stop MSOLAP$TPSAMA /y | stop VeeamEnterpriseManagerSvc /y | stop vapiendpoint /y |
Another technique used by most variants of Thanos based ransomware is to evade detection by finding and terminating processes for analysis tools by searching the list of keywords shown below:
| http analyzer stand-alone | NetworkTrafficView | CFF Explorer |
| fiddler | HTTPNetworkSniffer | protection_id |
| effetech http sniffer | tcpdump | pe-sieve |
| firesheep | intercepter | MegaDumper |
| IEWatch Professional | Intercepter-NG | UnConfuserEx |
| dumpcap | ollydbg | Universal_Fixer |
| wireshark | dnspy-x86 | NoFuserEx |
| wireshark portable | dotpeek | cheatengine |
| sysinternals tcpview | dotpeek64 | |
| NetworkMiner | RDG Packer Detector |
Further, it changes the configuration of specific services as shown below.
Figure 8: Screenshot of service configuration changes.
It deletes shadow copy using powershell command so the system is unable to recover data.
Command : "powershell.exe" & Get-WmiObject Win32_Shadowcopy | ForEach-Object { $_Delete(); }
File Encryption
Midas ransomware searches through each drive and directory and encrypts the files. It creates a random key and encrypts a file using Salsa20 algorithm. Then the Salsa20 key is encrypted by the RSA public key as shown in the screenshot below. The encryption key is encoded in base64 and appended to each impacted file. It also added FileMarker “GotAllDone” at the end of each encrypted file. The encrypted key is also saved in the Registry under “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\KEYID\myKeyID”. After encryption, it drops the “reload1.lnk” file to open a ransom note at every restart.
Path: "C:\\Users\\{Username}\\AppData\\Roaming\\Microsoft\\Windows\\Start Menu\\Programs\\Startup\\reload1.lnk".
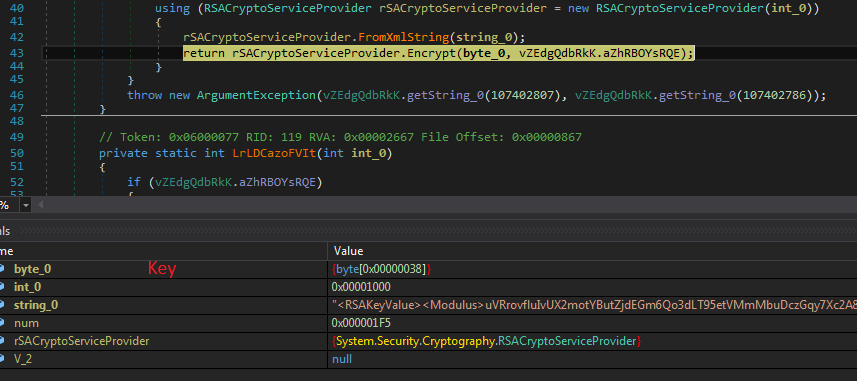
Figure 9: Screenshot of encrypting Salsa20 key with RSA public key.
It encrypts the file contained below extensions:
After encryption it appends “.{Targeted Company name}” extension and drops “RESTORE_FILES_INFO.hta and RESTORE_FILES_INFO.txt” ransom note. Below is the screenshot of the ransom note. RESTORE_FILES_INFO.hta doesn’t contain Key ID but RESTORE_FILES_INFO.txt contains key ID.
Figure 10: Ransom note of Midas
Cloud Sandbox Detection
Figure 11: Zscaler Cloud Sandbox detection of Midas ransomware
In addition to sandbox detections, Zscaler’s multilayered cloud security platform detects indicators at various levels.
Win32.Ransom.Thanos
https://threatlibrary.zscaler.com/?threatname=win32.ransom.thanos
Win32.Ransom.Prometheus
https://threatlibrary.zscaler.com/?threatname=win32.ransom.prometheus
Win32.Ransom.Spook
https://threatlibrary.zscaler.com/?threatname=win32.ransom.spook
Win32.Ransom.Haron
https://threatlibrary.zscaler.com/?threatname=win32.ransom.haron
Win32.Ransom.Midas
https://threatlibrary.zscaler.com/?threatname=win32.ransom.midas
MITRE ATT&CK Technique
|
ID |
Technique |
|
T1059 |
Command and Scripting Interpreter |
|
T1569.002 |
Service Execution |
|
T1112 |
Modify Registry |
|
T1562.001 |
Disable or Modify Tools |
|
T1010 |
Application Window Discovery |
|
T1057 |
Process Discovery |
|
T1518.001 |
Security Software Discovery |
|
T1083 |
File and Directory Discovery |
|
T1490 |
Inhibit System Recovery |
|
T1489 |
Service Stop |
|
T1486 |
Data Encrypted for Impact |
IOC
MD5:3767a7d073f5d2729158578a7006e4c4
About ThreatLabz
ThreatLabz is the security research arm of Zscaler. This world-class team is responsible for hunting new threats and ensuring that the thousands of organizations using the global Zscaler platform are always protected. In addition to malware research and behavioral analysis, team members are involved in the research and development of new prototype modules for advanced threat protection on the Zscaler platform, and regularly conduct internal security audits to ensure that Zscaler products and infrastructure meet security compliance standards. ThreatLabz regularly publishes in-depth analyses of new and emerging threats on its portal, research.zscaler.com.
Further Reading: Zscaler Ransomware Protection






