/ SD-WAN vs. MPLS: What's the Difference?
SD-WAN vs. MPLS: What's the Difference?
SD-WAN delivers a virtual private network over multiple internet connections, while MPLS is a private network service delivered by a telecom provider. Today, most organizations agree that SD-WAN is more cost-effective and flexible than MPLS.

What Is SD-WAN?
A software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) uses routing protocols and overlay tunnels to securely connect locations across various network types, including broadband internet, cellular and satellite links. It provides an efficient alternative to traditional private WANs, especially as organizations move away from on-premises data centers.
How Does SD-WAN Work?
SD-WAN improves application performance by dynamically routing traffic along the best available paths. It uses encrypted VPN tunnels to securely transfer data, prioritizing traffic based on business policies to ensure quality of service (QoS). These features enable direct, secure connections from branches to data centers, SaaS apps, and cloud services.
Key Features of SD-WAN
- Smart routing: Optimizes traffic paths for better app performance.
- Secure tunnels: Uses encrypted overlays to protect data.
- Traffic prioritization: Ensures QoS based on business needs.
- Multi-path support: Combines broadband, LTE, and other connections.
- Centralized control: Simplifies WAN management and monitoring.
Pros and Cons of SD-WAN
✔️ Lower last-mile costs, improved reliability and simpler management vs. traditional or hybrid WAN
✖️ Wider attack surface than private WAN solutions like MPLS, and harder to secure—often deployed with additional firewalls at each location
What Is MPLS?
Multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) is a private WAN service that routes data packets using labels instead of IP addresses. These labels control the path packets take, enabling faster delivery than traditional router-by-router forwarding. MPLS minimizes latency, reduces packet loss, and enhances QoS for critical traffic. It also ensures customer traffic stays private and segmented from the public internet.
How Does MPLS Work?
MPLS uses labels to send traffic along predefined paths, unlike IP routing, where each router independently chooses the next hop. MPLS routers group similar data packets, reducing network congestion and latency. However, MPLS lacks built-in security and must backhaul traffic to a security stack, which can increase latency.
Key Features of MPLS
- Label-based routing: Uses labels for faster, predefined traffic paths.
- Quality of service (QoS): Prioritizes critical app traffic.
- Low latency: Reduces delay by avoiding traditional routing processes.
- Scalability: Supports high data volumes for large networks.
- Security gaps: Requires external measures for encryption.
Pros and Cons of MPLS
✔️ Reliable performance, low latency, and strong QoS for critical apps vs. public internet connections
✖️ Higher costs, less flexibility, and limited cloud compatibility vs. modern solutions like SD-WAN
MPLS vs. SD-WAN: Which Is the Right Choice for Your Organization?
Ultimately, the choice between SD-WAN and MPLS depends on your organization's needs and priorities. Here’s a quick breakdown of some key considerations:
- Cost: MPLS relies on expensive private circuits, while SD-WAN reduces expenses by utilizing cost-effective broadband internet.
- Performance: MPLS offers consistent, low-latency performance, ideal for real-time applications. SD-WAN dynamically routes traffic for strong performance but depends on the quality of internet connections, which can vary.
- Security: MPLS provides private connections but lacks built-in encryption. SD-WAN integrates encrypted tunnels and cloud-delivered security, making it better suited for dynamic, security-focused environments.
- Scalability: SD-WAN scales easily and allows swift deployment of new locations using virtual infrastructure. MPLS is less flexible and requires significant time and cost to expand.
- Cloud and remote work: MPLS struggles to efficiently support cloud apps and remote users, often introducing latency and costs through centralized routing. SD-WAN offers local internet breakouts and seamless cloud integration for better performance.
Benefits of SD-WAN Compared to MPLS
- Lower costs: Uses public internet instead of costly dedicated circuits.
- Greater flexibility: Virtualized infrastructure enables rapid changes.
- Higher performance: Prioritizes critical traffic and eliminates backhauling.
- Greater simplicity: Zero-touch provisioning automates configuration.
- Stronger security: Encrypted end-to-end tunnels and cloud security integration.
- SASE support: Integrates networking and cloud-delivered security, such as secure access service edge (SASE), for modern environments.
MPLS may work for organizations that need predictable, low-latency performance for mission-critical applications, and little else. That said, SD-WAN's benefits in cost-efficiency, flexibility, and cloud readiness make it the preferred option for distributed and dynamic environments.
Industry Trends and the Future of WAN
The rise of SASE and zero trust is transforming WAN by combining networking and security to support distributed workforces. As cloud adoption grows, traditional WANs like MPLS can’t meet demands for flexibility or scalability. SD-WAN solutions are emerging as the preferred choice, offering direct cloud access and advanced security for modern needs.
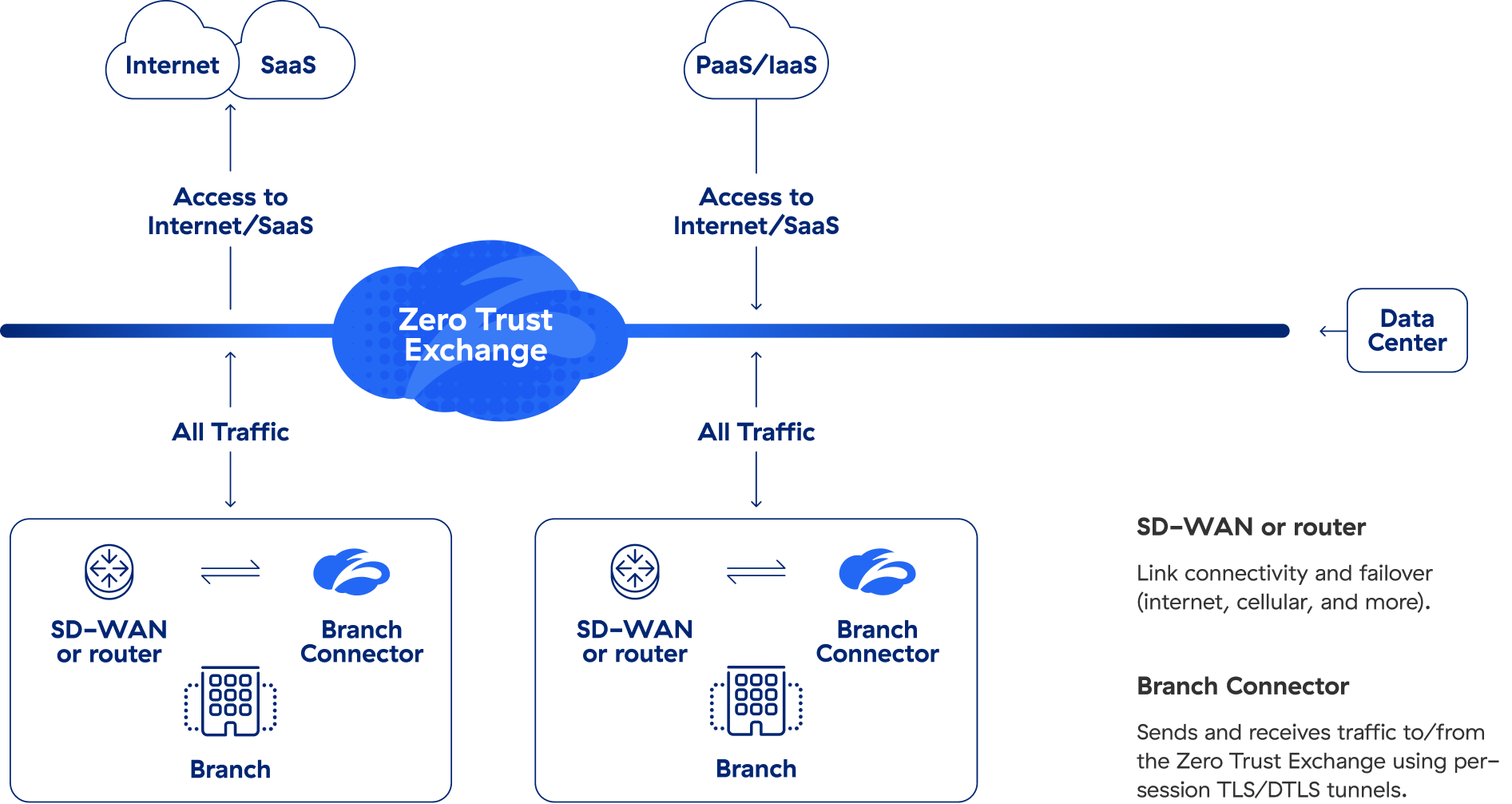
Even so, traditional SD-WAN extends the same implicit trust inherent to all IP networks, enabling unrestricted lateral movement that facilitates the spread of cyberthreats such as ransomware. To provide truly secure SD-WAN connectivity for users, servers, and IoT/OT devices anywhere, you need to combine it with zero trust.
How Zscaler Can Help
Zscaler Zero Trust SD-WAN combines secure SD-WAN with the power of a zero trust architecture.
Replace traditional branch WAN solutions such as MPLS by bringing zero trust principles to every user, server, and IoT/OT device. With its direct-to-cloud architecture, Zscaler eliminates the attack surface and lateral movement with a non-routable WAN network.
Modernize branch and data center connectivity with quicker SaaS and cloud app deployments, local internet breakouts, and no more site-to-site VPNs. With integrated and automated connectivity and security, Zscaler reduces complexity and cost and provides a faster, smarter, and more secure alternative to legacy networking and security solutions.
Zero Trust SD-WAN Real-World Use Cases
Replace Site-to-Site VPNs
Eliminate complex site-to-site VPNs or hub-and-spoke networks, improving performance.
Accelerate and Secure M&A Integration
Enable branch offices in one IT environment to quickly connect to private apps in another, with no need to integrate networks.
Secure Access to OT Resources
Provide clientless browser-based access to SSH/RDP ports on OT assets for third parties while removing exposed ports or VPN endpoints, eliminating the attack surface.
Discover and Classify IoT Devices
Get deeper visibility and insights into IoT devices at the branch. Automatically classify devices based on traffic profiles, and easily manage policy for IoT traffic.
Achieve Zero Trust SASE
Reduce business risk and network complexity with Zero Trust SASE, built on Zero Trust SD-WAN.
Connect and protect your branches with the simple, scalable, secure Zero Trust SD-WAN.
Suggested Resources
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
SD-WAN can replace MPLS in most cases, but organizations with MPLS-specific compliance or privacy requirements can use both. MPLS circuits can also serve as SD-WAN paths when required.
SD-WAN uses multiple connection types, while MPLS relies on static circuits. This makes SD-WAN more cost-effective, flexible, secure, and better suited for distributed organizations/workforce.
Yes, SD-WAN can use MPLS circuits as part of its virtual overlays, allowing organizations to continue using their existing MPLS infrastructure while addressing its limitations.


