Zscaler Blog
Get the latest Zscaler blog updates in your inbox
Subscribe
Bringing Zero Trust to Branches
Over the past five years, the tech industry has undergone significant transformation. Among the myriad changes in how organizations approach technology to gain a competitive edge, three primary shifts have had profound impacts:
- Migration of apps from traditional data centers to the cloud (the rise of SaaS)
- Hybrid workforce models, where employees operate from both regional offices and remote locations
- Proliferation of IoT/OT devices in factories and branch offices
Many enterprises are finding that limitations in their WAN infrastructure and gaps in network security impede their ability to deal with these three shifts.
Traditional SD-WANs expand the attack surface and allow lateral threat movement. They connect various sites through site-to-site VPNs or routed overlays, establishing implicit trust that grants unrestricted access to critical business resources, even for compromised entities. Moreover, coarse-grained segmentation policies allow threats to move easily within the network. With the rising number of threats and the adoption of IoT/OT devices, which are often invisible to the network, organizations need to ensure their WAN infrastructure adheres to zero trust principles.
Traditional WAN infrastructure consists of multiple point products such as routers, firewalls, and VPNs, which can add up to substantial management challenges. Hence, organizations undertaking branch transformation need a solution that follows a “thin branch, thick cloud” model to reduce management complexities.
Zscaler Zero Trust SD-WAN securely connects branches, factories, and data centers without the complexity of VPNs, ensuring zero trust access for users, IoT/OT devices, and servers. Using Zero Trust SD-WAN, enterprises can build a thin branch that eliminates unnecessary devices with a simple plug-and-play appliance that can be deployed using only an internet connection.
Zero Trust SD-WAN eliminates business risk
Unlike traditional SD-WANs that extend the network to remote sites, clouds, and third parties, Zero Trust SD-WAN connects users, IoT/OT devices, and applications to resources they are entitled to access, without using routed overlays. This creates a zero trust network that eliminates the attack surface and prevents lateral threat movement. Since all traffic is proxied through Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange, there are no publicly exposed IP addresses or VPN ports for hackers to compromise.
A recent Zscaler ThreatLabz report revealed a 400% increase in IoT and OT-based malware attacks since 2022, underscoring the need for organizations to have greater visibility and security around IoT/OT devices deployed in their networks. Often overlooked and invisible, IoT/OT is not adequately addressed when administrators design security policies for branch users, but as the ThreatLabz report shows, these devices represent a significant threat vector.
Zero Trust SD-WAN provides complete device visibility, giving organizations a detailed view of all their IoT/OT devices as well as insights into the applications with which they communicate. Moreover, administrators no longer need separate policies for users and devices since the same policies can be applied consistently to both.
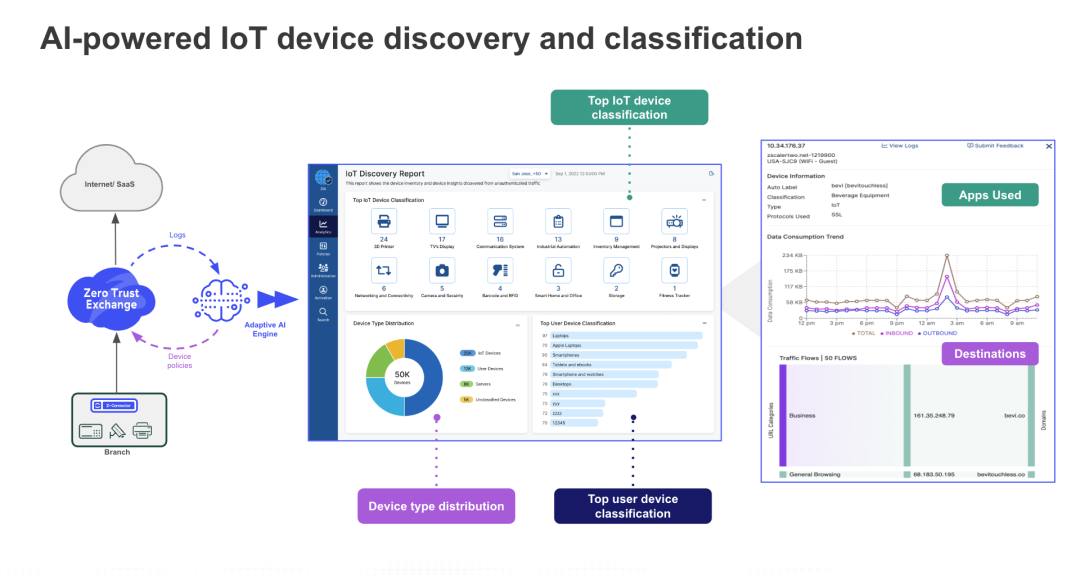
Figure 2: IoT device discovery and classification
Many organizations have server-to-client communication use cases. For instance, a print server in a data center may need to issue a print command to a remote printer in branch location. With Zero Trust SD-WAN, organizations don’t have to worry about exposed service ports that a hacker could exploit to breach the network. All branch communication is proxied through Zero Trust Exchange, which stitches the connection between the print server and the remote printer. Extending zero trust security to all entities, such as users, IoT/OT devices, and servers, enhances overall security.
Zero Trust SD-WAN replaces site-to-site VPNs
Traditional SD-WANs connect sites (e.g., branches, factories, data centers) using IPsec VPN tunnels. Routed overlays allow any device to communicate with any other device, server, or app, ensuring reachability between users, devices, and apps—reachability that hackers can exploit to easily access other resources in the network.
With Zero Trust SD-WAN, branch traffic is forwarded directly to the Zero Trust Exchange, where Zscaler Internet Access (ZIA) or Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) policies can be applied for full security inspection and identity-based access control. Zero Trust SD-WAN dramatically simplifies branch communication with a zero trust network overlay that allows for flexible forwarding and simple policy management.
Zero Trust SD-WAN simplifies mergers and acquisitions
Combining two separate businesses into one entity can provide enhanced efficiency, increased market presence, and other advantages. However, integrating new systems and routing domains into the existing environment can be a slow, painful process that takes many months to complete. With Zscaler, the entire M&A integration process can be far simpler and faster.
Zero Trust SD-WAN communicates only to the Zero Trust Exchange, eliminating the need to merge routing domains between existing and acquired sites. By deploying Zero Trust SD-WAN at an acquired site, enterprises can steer traffic to Zero Trust Exchange, which brokers the connection from the other end for secure communication. This results in successful day-one operation and onboarding of new sites in a matter of just weeks, or even days.
How does this all work?
- Apps defined in the ZPA portal are assigned a synthetic IP address.
- Once a user initiates a connection to the new app using the synthetic IP, Zero Trust SD-WAN at that branch site sends traffic to the Zero Trust Exchange.
- In the acquired site, where the app is hosted, the App Connector (built into Zero Trust SD-WAN) initiates an inside-out connection to the Zero Trust Exchange.
- The Zero Trust Exchange brokers the connection from the user to the app.
Conclusion
Organizations need a networking solution that protects them from today’s growing cyberthreats, but traditional SD-WANs increase security risk and networking complexity. In contrast, Zero Trust SD-WAN brings zero trust principles to WANs by securely connecting users, IoT/OT devices, and servers. To enhance the security of branches, factories, and data centers, organizations must transition from traditional flat networks with implicit trust to zero trust networks. Adopting Zero Trust SD-WAN offers numerous benefits, such as mitigating cyber risk, lowering cost and complexity, enhancing business agility, and implementing a single-vendor SASE solution.
For more information, please visit the Zscaler Zero Trust SD-WAN webpage.
Was this post useful?
Get the latest Zscaler blog updates in your inbox
By submitting the form, you are agreeing to our privacy policy.




