WordPress is by far the most popular content management system (CMS) and, because of its wide usage, it is also popular among cybercriminals. Most of the WordPress sites that have been compromised are the result of attackers exploiting vulnerable versions of the plugins used.
A stored cross-site script vulnerability was discovered last week in the popular WordPress Live Chat Support plugin. The vulnerability allows an unauthenticated attacker to update the plugin settings by calling an unprotected "admin_init hook" and injecting malicious JavaScript code everywhere on the site where Live Chat Support appears. All versions of this plugin prior to version 8.0.27 are vulnerable. The patched version for this vulnerability was released on May 16, 2019, and has been fixed for version 8.0.27 and higher.
ThreatLabZ researchers recently discovered what may be the first campaign in which attackers are exploiting the Live Chat Support plugin vulnerability and injecting a malicious script that is responsible for malicious redirection, pushing unwanted pop-ups and fake subscriptions. While it is not yet seen as a widespread attack, the number of compromised websites is growing (at the end of this blog there is a link to the names of the compromised sites).
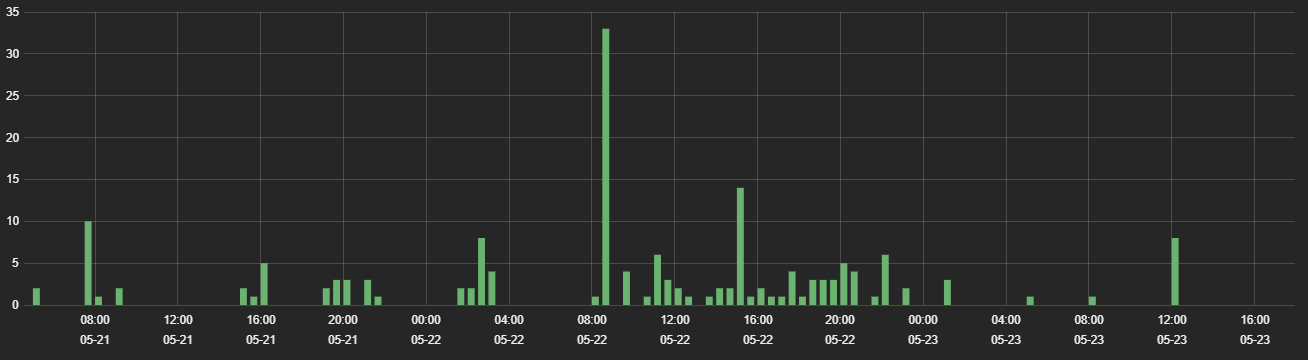
Fig 1: Hits of the compromised WordPress sites
Fig 2: WordPress site using a vulnerable version of the Live Chat Support plugin
Fig 3: Obfuscated script injected in the compromised WordPress site
Fig 4: Deobfuscated version of the injected script
The injected script sends a request to the URL hxxps://blackawardago[.]com to execute the main script.
Fig 5: Request and response to the hxxps://blackawardago[.]com
After the execution of the above script, the victim is redirected to multiple URLs, mainly related to pushing unwanted popup ads and fake error messages.
Fig 6: Highlighted (red) multiple redirected URLs after the execution of the malicious script.
Fig 7: Popups after execution of the malicious script
The domain that hosts the malicious script is a newly created domain hosted on a dedicated IP address.
Fig 8: Whois information of the domain
Conclusion
Cybercriminals actively look for new vulnerabilities in popular content management systems such as WordPress and Drupal, as well as popular the plugins that are found in many websites. An unpatched vulnerability in either the CMS or associated plugins provides an entry point for attackers to compromise the website by injecting malicious code and impacting the unsuspecting users visiting these sites.
It is critical for website owners to apply the security update if they are using the vulnerable plugin, particularly because it is a pre-auth vulnerability and can lead to widespread compromise.
The Zscaler ThreatLabZ team is actively tracking and reviewing all such malicious campaigns to ensure that our customers are protected.
IOCs
blackawardago[.]com
216[.]10[.]243[.]93
List of compromised sites is available here.
















