
CXO Monthly Roundup, March 2025: AI Security Report, CoffeeLoader analysis, and more
Apr 1, 2025
The March edition of the CXO Monthly Roundup from Zscaler ThreatLabz.
Welcome to the new CXO Monthly Roundup, an expansion from "CISO" due to the interest in this ongoing series from all technical C-level readers. We feature the latest threat research from the Zscaler ThreatLabz team and other cybersecurity insights.
In this edition, we unpack the highlights from our recent 2025 AI Security Report, which contains relevant insights for the entire enterprise. Plus, read our technical analysis of the CoffeeLoader malware, learn about recently discovered vulnerabilities, and explore emerging threats.
Zscaler ThreatLabz 2025 AI Security Report: Balancing Innovation and Protection
The ThreatLabz 2025 AI Security Report examines how enterprises are integrating artificial intelligence (AI) solutions while confronting emerging security challenges. Drawing from an extensive analysis of 536.5 billion AI/ML transactions processed through the Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange, this report highlights key findings and trends shaping the interplay between AI innovation and organizational security strategies. The research spans activity across 800+ known AI and ML applications collected during the period of February to December 2024.
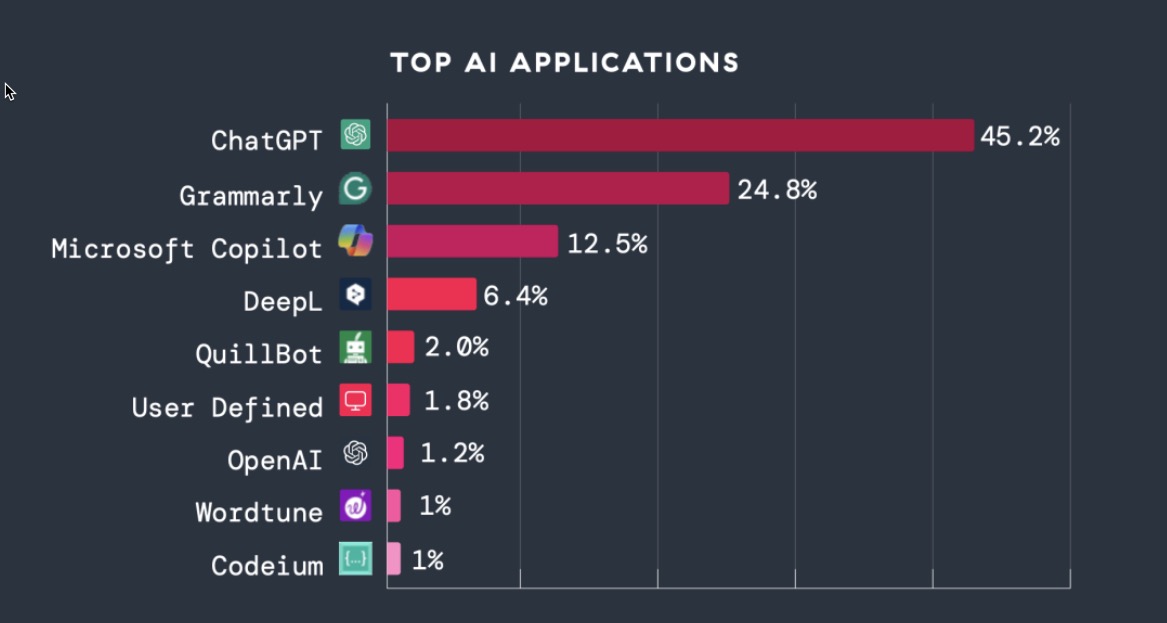
Figure 1: Top AI applications by transaction volume
Productivity wins
By far, productivity assistants experienced the highest transaction volume compared to other AI-related applications.
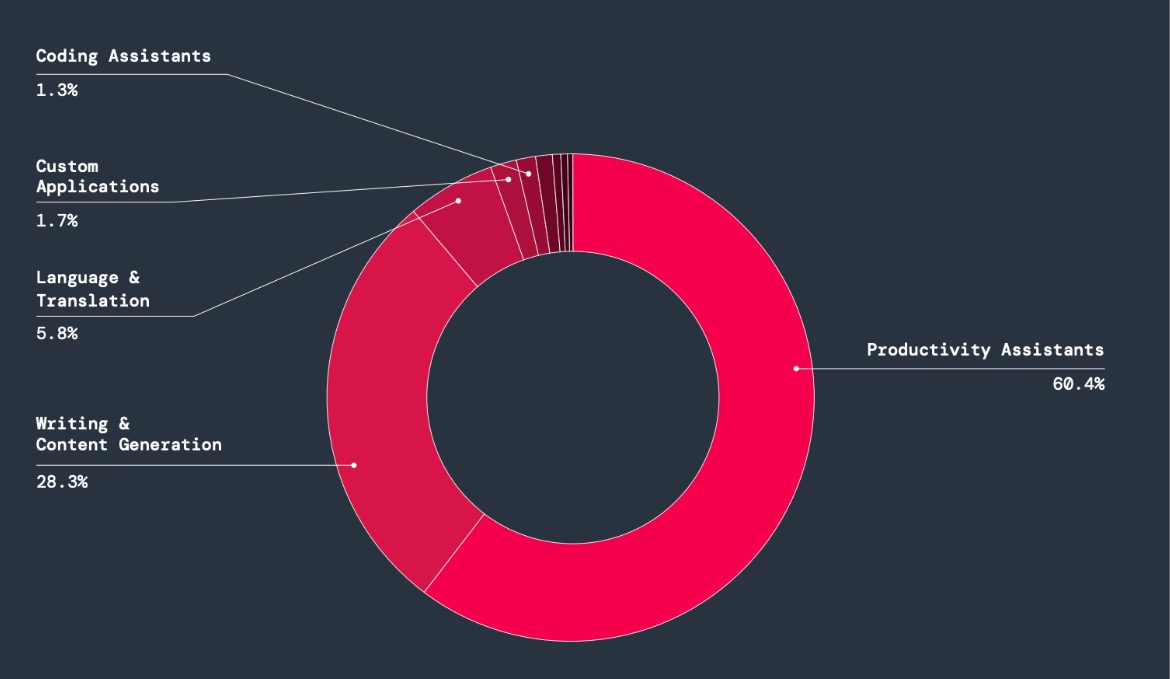
Figure 2: Transactions by application category
Key findings:
- AI adoption explodes: AI/ML transactions grew 36x YoY (+3,464.6%), driven by tools like ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot.
- Top sectors: Finance & Insurance (28.4%) and Manufacturing (21.6%) led AI usage, followed by Technology, Healthcare, and Government.
- High transaction blockage: 59.9% of AI/ML traffic was blocked due to data security concerns and governance barriers.
- Global leaders: The U.S. and India generated the most AI traffic with strong adoption across major industries.
- Rising AI threats: Cybercriminals are weaponizing AI for phishing, malware, and deepfakes, posing growing risks.
Secure AI Adoption with Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange
The Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange empowers organizations to securely adopt AI/ML technologies while minimizing risks. Built on the principles of Zero Trust architecture, it offers advanced security for both internal and external AI applications.
Key capabilities include:
- Real-time policy enforcement to ensure compliant and secure AI usage.
- Comprehensive visibility into AI application behavior, usage patterns, and enterprise-wide activity.
- Data protection to prevent intellectual property theft, privacy breaches, and data loss to generative AI apps.
- Risk-based access controls with AI app scoring to manage access selectively and mitigate security risks.
- Threat detection and response to identify and block AI-enabled attacks.
CoffeeLoader
Zscaler ThreatLabz published a technical analysis of CoffeeLoader, a new and sophisticated malware family that implements features designed to bypass modern security software, bearing a close resemblance to SmokeLoader. CoffeeLoader uses techniques like call stack spoofing, sleep obfuscation, and the use of Windows fibers to evade endpoint security software. In addition, CoffeeLoader employs a GPU-based packer known as Armoury, a novel approach that sets it apart from most malware, which traditionally relies on the CPU for execution.
Armoury uses the OpenCL library to execute decryption code on the GPU, bypassing the need for specific hardware or dependencies. The packer performs XOR-based decryption by combining hardcoded strings to generate a key. The decrypted shellcode is then passed back to the CPU, which executes the malicious CoffeeLoader payload. By offloading critical computations to the GPU, Armoury avoids many detection mechanisms and complicates analysis in virtual environments where GPU activity is often not emulated.
To learn about CoffeeLoader’s other evasion techniques, network protocol, and its similarities with SmokeLoader, check out our blog post.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage – Zscaler Internet Access (Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, SSL Inspection)
Multiple Critical Vulnerabilities In the Wild
IngressNightmare Vulnerabilities (CVE-2025-24513, CVE-2025-24514, CVE-2025-1097, CVE-2025-1098, and CVE-2025-1974)
A group of five security vulnerabilities have been disclosed in the Ingress NGINX Controller for Kubernetes that could result in attackers executing arbitrary code. The CVE-2025-24513, CVE-2025-24514, CVE-2025-1097, CVE-2025-1098, and CVE-2025-1974 vulnerabilities have been collectively nicknamed IngressNightmare by the security firm that discovered them.
- Severity: Assigned a CVSS score of 9.8 (critical).
- Affected Versions: The IngressNightmare vulnerabilities affect versions of the Ingress NGINX Controller for Kubernetes prior to the patched versions:
- Ingress NGINX Controller prior to v1.12.1
- Ingress NGINX Controller prior to v1.11.5
- Recommendations: If an immediate upgrade is not possible:
- Implement strict network policies to ensure that only the Kubernetes API Server can communicate with the admission controller.
- Disable the admission controller component in the Ingress NGINX Controller temporarily if an upgrade is not immediately feasible.
Zscaler platform and services are not impacted by this vulnerability.
Apache Tomcat Path Equivalence Vulnerability (CVE-2025-24813)
CVE-2025-24813 is a path equivalence vulnerability enabling remote code execution (RCE), information disclosure, and content injection on Apache Tomcat servers. Exploited in specific configurations, CVE-2025-24813 could allow attackers to upload malicious files and execute arbitrary commands, ultimately taking control over compromised servers.
- Severity: Initially rated at 5.5 (medium), later raised to 9.8 (critical) by NVD following active exploitation.
- Affected Versions:
- Apache Tomcat 11.0.0-M1 to 11.0.2
- Apache Tomcat 10.1.0-M1 to 10.1.34
- Apache Tomcat 9.0.0-M1 to 9.0.98
- Recommendations:
- Immediately upgrade to patched versions (11.0.3+, 10.1.35+, or 9.0.99+).
Zscaler platform and services are not impacted by this vulnerability.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage – Zscaler Private Access (App Protection, Deception) and Zscaler Workload Segmentation
Next.js Middleware Authorization Bypass Flaw (CVE-2025-29927)
CVE-2025-29927 is a flaw allowing attackers to exploit specially crafted x-middleware-subrequest headers to bypass authorization checks in Next.js Middleware. CVE-2025-29927 could enable attackers to gain unauthorized access, steal data, escalate privileges, perform cache poisoning, and more.
- Severity: Rated 9.1 (critical).
- Affected Versions:
- > 11.1.4 <= 13.5.6 (No patch available)
- > 12.0 < 12.3.5 (Patched in 12.3.5)
- > 13.0 < 13.5.9 (Patched in 13.5.9)
- > 14.0 < 14.2.25 (Patched in 14.2.25)
- > 15.0 < 15.2.3 (Patched in 15.2.3)
- Recommendations: Upgrade to the patched versions as listed above.
- For applications running version greater than 11.1.4 and less than or equal to 13.5.6, where no secure version is available, configure load balancers or web servers to block external requests containing the x-middleware-subrequest header from reaching the Next.js application.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage – Zscaler Private Access (App Protection, Deception)
Prevalent Threat Updates
Emerging Threat: AiLock Ransomware Group
This month, Zscaler ThreatLabz identified a new ransomware group calling themselves AiLock, leveraging sophisticated extortion tactics targeting enterprise networks. Their ransom note, newly added to our GitHub repository, reveals unique elements of their operations:
- Regulatory and competitor fears: AiLock plays on the fear of privacy regulations by threatening to report data breaches to regulators and alert competitors if businesses don’t cooperate.
- Intense deadlines: The group gives victims just 72 hours to respond and 5 days to pay. They claim failing to act will lead to public data leaks and the destruction of recovery tools.
- A "helpful" offer: AiLock promises to keep things confidential, provide "deletion logs," and even offer IT security tips for the future.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage – Zscaler Internet Access (Advanced Threat Protection, Advanced Cloud Sandbox, SSL Inspection) and Zscaler Private Access (Deception, Identity Protection)
About ThreatLabz
ThreatLabz is the embedded research team at Zscaler. This global team includes security experts, researchers, and network engineers responsible for analyzing and eliminating threats across the Zscaler security cloud and investigating the global threat landscape. The team shares its research and cloud data with the industry at large to help promote a safer internet.
The Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange
Zscaler manages the world’s largest security cloud. Each day, Zscaler blocks over 150 million threats to its more than 8,650 customers, securing over 500 billion web transactions daily. The Zscaler ThreatLabz security research team uses state-of-the-art AI/ML and machine-learning technology to analyze Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange traffic and share its findings.
Recommended
