
CISO Monthly Roundup, August/September 2024: Copybara, BlindEagle, typosquatting, and Zenith Live ‘24 keynote
Oct 8, 2024
In the latest CISO Monthly Roundup, Zscaler CSO Deepen Desai and ThreatLabz provide a technical analysis of the Copybara Android malware, a targeted BlindEagle campaign, and more.
The CISO Monthly Roundup provides the latest threat research from the ThreatLabz team, along with CISO insights on cyber-related subjects. In this edition, we explore a variant of Copybara Android malware active since November 2023, spotlight the BlindEagle attack chain used to target the Columbian insurance sector, present original research on the top typosquatting domains and the brands they impersonate, plus themes from my keynote session from Zenith Live '24 in the APAC region.
A study into the latest variant of Copybara
ThreatLabz recently looked at a new version of the Copybara Android malware. This version came out in November 2021 and has been active since November 2023. This malware is spread through vishing attacks, and it exploits the Android Accessibility Service feature to gain control over infected devices.
The latest variant uses the MQTT protocol for communication with its command-and-control (C2) server. Copybara downloads phishing pages that mimic popular cryptocurrency exchanges and financial institutions, deceiving victims into entering their credentials.
Key findings include:
- Internet of Things (IoT) optimized communication: The latest Copybara variant leverages the MQTT protocol, a lightweight messaging system optimized for efficient communication between devices with limited resources or constrained network bandwidth. This makes it particularly suited for IoT devices.
- Abuse of Accessibility Service: The malware abuses the Android Accessibility Service feature to gain granular control over the device, making it difficult for users to uninstall the malware and allowing it to execute its malicious activities in the background.
- Malware capabilities: Copybara has a wide range of capabilities, including keylogging, audio and video recording, SMS hijacking, screen capturing, and remote control of the infected device. It also downloads phishing pages that imitate financial institutions and cryptocurrency exchanges to steal credentials.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage - Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, Advanced Cloud Firewall, SSL Inspection, Deception
BlindEagle Targets Colombian Insurance Sector with BlotchyQuasar
In June 2024, ThreatLabz identified new activity from BlindEagle (also known as AguilaCiega, APT-C-36, and APT-Q-98), an APT group targeting government and financial sectors in Colombia and Ecuador. This campaign delivered modified QuasarRAT, called BlotchyQuasar, through phishing emails impersonating the Colombian Tax and Customs National Authority (DIAN). The malware targeted the Colombian insurance sector, aiming to steal payment data. The figure below shows the BlindEagle attack chain.
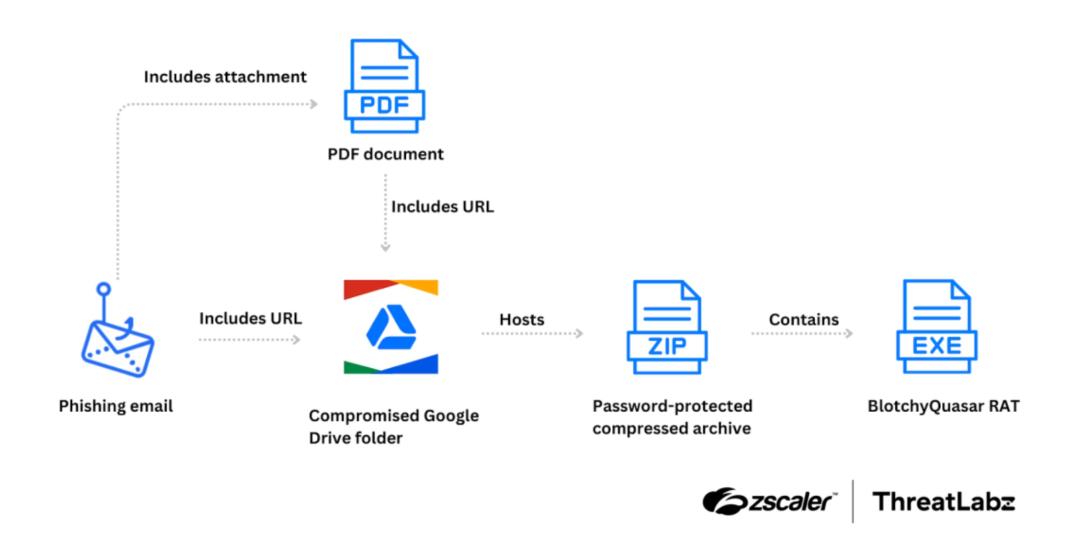
The attack chain started with a phishing email leading to a ZIP archive containing the BlotchyQuasar executable. Below is an example of the phishing email.

The heavily obfuscated malware logged keystrokes and monitored banking activities. The C2 server was retrieved via a Pastebin link, and malicious domains tied to the campaign revealed links to compromised routers in Colombia. This campaign highlights BlindEagle’s focus on South American organizations and its use of custom, enhanced RATs to steal financial data.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage - Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, Advanced Cloud Firewall, SSL Inspection, Deception, Identity Protection.
Phishing Via Typosquatting and Brand Impersonation: Trends and Tactics
The ThreatLabz team has been monitoring typosquatting and brand impersonation trends to analyze phishing attacks. These techniques, which mimic popular websites and brands, exploit user mistakes to steal data or deliver malware.
From February 2024 to July 2024, ThreatLabz analyzed over 30,000 lookalike domains and identified 10,000 as malicious. The most targeted brands were Google, Microsoft, and Amazon, accounting for almost 75% of phishing domains, as shown below.
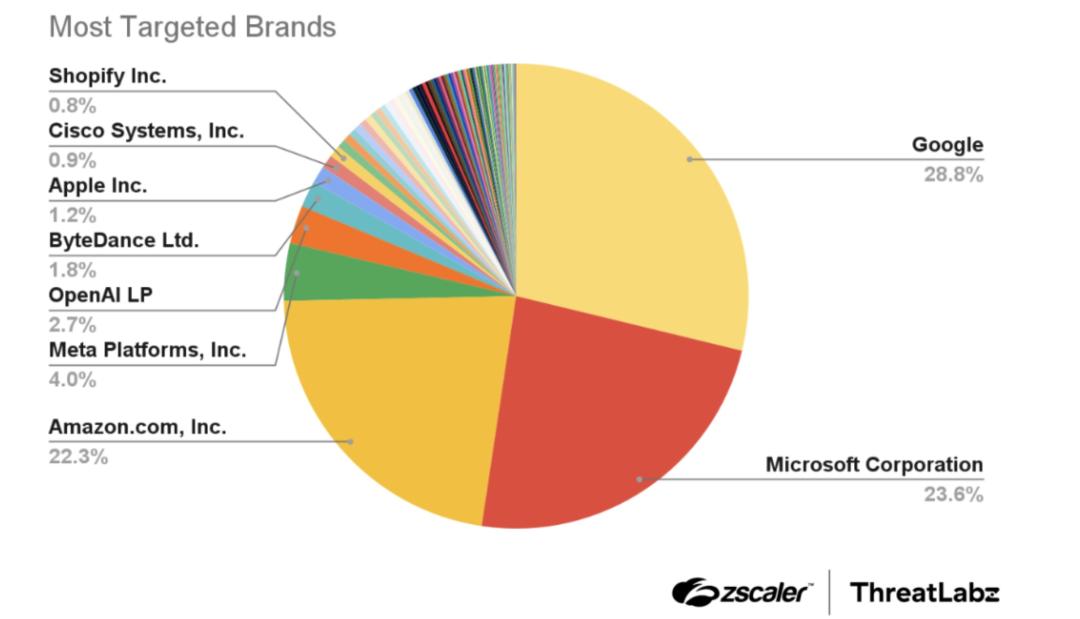
The Internet Services sector was the top target, followed by Professional Services and Online Shopping. Attackers often use free Let’s Encrypt certificates to appear legitimate, and the .com TLD was the most commonly abused. Our analysis also highlights case studies showing malware distribution, credential theft, scams, and C2 communication linked to typosquatting domains.
ThreatLabz is committed to monitoring and blocking these threats to protect users from phishing attacks.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage - Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, SSL Inspection
Zenith Live ‘24 APAC: Cyber Risk Management in the Age of AI
Zenith Live in the Asia Pacific (APAC) region is a Zscaler flagship global event bringing together employees, customers, and partners to explore the latest trends in cybersecurity.
AI-powered attacks and ransomware surge
In my keynote, I highlighted the growing number of AI-fueled attacks. This year alone, one deepfake vishing campaign, where cybercriminals use advanced voice cloning to impersonate key executives, lost an organization $25 million. Over 10,000 organizations were impacted by VPN zero-day attacks in 2023 all told, a significant rise compared to previous years. These attacks are often facilitated by critical vulnerabilities being exploited in outdated systems within IT environments where legacy devices are still in use. Ransomware, too, remains a threat. In 2023, cybercriminals collected $1.1 billion from ransomware attacks, and, with a historic payout of $75 million in 2024, their impact is only increasing.
Launching an attack with just one prompt
During my presentation, I shared an example of how a threat actor could use a single prompt to instruct a rogue generative AI module to perform the entire attack chain – from external attack surface discovery to data exfiltration. With just one prompt, the threat actor can scan for public vulnerabilities, scrape social media networks to identify compromised employee personas, and infiltrate AI/ML development and production environments to steal sensitive data. In fact, nation-state threat actors are already targeting these environments because of the high-value data they hold.
How Zscaler Can Help with AI-Driven Solutions
- Proactively predict and prevent breaches: The Zscaler Breach Predictor uses AI/ML models to identify potential breach scenarios before they escalate by integrating endpoint indicators, east-west traffic insights, and global threat intelligence. It utilizes policy context to train large language models (LLMs) specific to your environment, enabling accurate predictions.
- Minimize attack surface: Zscaler reduces the attack surface by using zero trust architecture that hides applications behind the Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange (ZTE) to prevent discovery via the internet. By verifying identity and granting access on a per-request basis, Zscaler limits the opportunities for threat actors to exploit vulnerabilities. It also eliminates the need for inbound VPNs for remote users, providing secure, direct access to applications without exposing the network.
- Prevent compromise: In addition to inspecting all traffic, Zscaler employs proactive inline sandboxing to detect and block suspicious files before they reach users, ensuring unknown threats are stopped in real-time. Additionally, browser isolation protects users by rendering potentially malicious websites in a secure environment, preventing compromise even if users interact with risky content.
- Prevent lateral movement: The Zscaler Credential Exposure Detection solution, powered by AI, continuously monitors and analyzes credential usage across environments to identify potential exposures in real time. With AI-powered dynamic honeypots, Zscaler enables security teams to deploy one-click decoys in generative AI and LLM environments, diverting attacks while gathering critical threat intelligence and protecting sensitive data. In addition to enabling segmentation and turning on Zero Trust app access in the office.
- Prevent data loss: Zscaler’s Data Loss Protection (DLP) solution ensures that sensitive data is monitored and protected, preventing the unauthorized movement of data and restricting attackers from accessing or exfiltrating valuable information.

Zscaler Business Continuity in the Wake of Major IT and Security Outages
The Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange is a mission-critical service, so it is unsurprising that we received a flurry of calls following these incidents from concerned customers who wanted to understand whether Zscaler is exposed to a risk similar to CrowdStrike’s. We advised our customers and prospects at length in an oversubscribed series of CXO briefings and a public Preventing Cloud Outages Webinar.
Discover how Zscaler is ensuring the resilience of the world’s largest security cloud with this on-demand webinar or read a summary.
About ThreatLabz
ThreatLabz is the embedded research team at Zscaler. This global team includes security experts, researchers, and network engineers responsible for analyzing and eliminating threats across the Zscaler security cloud and investigating the global threat landscape. The team shares its research and cloud data with the industry at large to help promote a safer internet.
The Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange
Zscaler manages the world’s largest security cloud. Each day, Zscaler blocks over 150 million threats to its 7300+ customers, securing over 300 billion web transactions daily. The Zscaler ThreatLabz security research team uses state-of-the-art AI/ML and machine-learning technology to analyze Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange traffic and share its findings.
What to read next:
Zero Trust & AI Cyber Innovation Keynote - Zenith Live APJ 2024
Preventing Cloud Outages [video briefing]
Recommended
